Cloning, expression analysis, and RNA interference study of a HORMA domain containing autophagy-related gene 13 (ATG13) from the coleopteran beetle, Tenebrio molitor
- PMID: 26136688
- PMCID: PMC4470068
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00180
Cloning, expression analysis, and RNA interference study of a HORMA domain containing autophagy-related gene 13 (ATG13) from the coleopteran beetle, Tenebrio molitor
Abstract
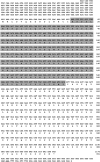
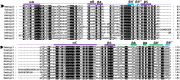
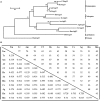
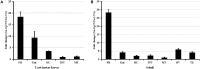
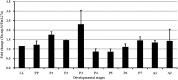
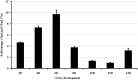
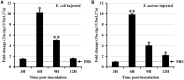
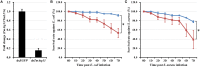
Autophagy is a process that is necessary during starvation, as it replenishes metabolic precursors by eliminating damaged organelles. Autophagy is mediated by more than 35 autophagy-related (Atg) proteins that participate in the nucleation, elongation, and curving of the autophagosome membrane. In a pursuit to address the role of autophagy during development and immune resistance of the mealworm beetle, Tenebrio molitor, we screened ATG gene sequences from the whole-larva transcriptome database. We identified a homolog of ATG13 gene in T. molitor (designated as TmATG13) that comprises a cDNA of 1176 bp open reading frame (ORF) encoding a protein of 391 amino acids. Analyses of the structure-specific features of TmAtg13 showed an intrinsically disordered middle and C-terminal region that was rich in regulatory phosphorylation sites. The N-terminal Atg13 domain had a HORMA (Hop1, Rev7, and Mad2) fold containing amino acid residues conserved across the Atg13 insect orthologs. A quantitative reverse-transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed that TmATG13 was expressed ubiquitously during all developmental stages of the insect. TmATG13 mRNA expression was high in the fat body and gut of the larval and adult stages of the insect. The TmATG13 transcripts were expressed at a high level until 6 days of ovarian development, followed by a significant decline. Silencing of ATG13 transcripts in T. molitor larvae showed a reduced survivability of 39 and 38% in response to Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus infection. Furthermore, the role of TmAtg13 in initiating autophagy as a part of the host cell autophagic complex of the host cells against the intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes is currently under study and will be critical to unfold the structure-function relationships.
Keywords: ATG13; HORMA domain; RNA interference; Tenebrio molitor; autophagy; expression analysis.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

