Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the lung treated with crizotinib: A case report
- PMID: 26137041
- PMCID: PMC4467348
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2015.3003
Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the lung treated with crizotinib: A case report
Abstract
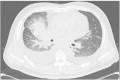
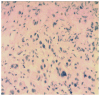
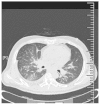
Primary signet-ring cell adenocarcinoma (SRCA) of the lung is an extremely rare subtype of lung adenocarcinoma with a poor prognosis. The presence of an SRC component is considered to be a prominent clinicopathological characteristic of EML4-ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Crizotinib, an anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor, has been approved for the treatment of EML4-ALK NSCLC by previous studies, but its effect on SRCA, an extremely rare subtype of lung adenocarcinoma, has yet to be elucidated. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the clinical response of SRCA to crizotinib, and examine the potential use of crizotinib as a treatment for the carcinoma. A 43-year-old male was admitted to the Qingdao Municipal Hospital (Qingdao, China) with dyspnea. Chest computed tomography (CT) revealed a mass in the middle lobe of the right lung. Transbronchial lung biopsies revealed the presence of SRCA (70%) mixed with poorly-differentiated adenocarcinoma (30%). Immunohistochemically, the SRCA cells were positive for cytokeratin (CK)7 and thyroid transcription factor-1, and negative for CK20. An inversion of the EML4-ALK gene was detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization and crizotinib was injected by nasogastric tube. The patient was highly responsive to crizotinib. The symptoms of dyspnea were relieved and the volumes of pericardial and pleural effusion were gradually reduced. A CT scan revealed lung tumor regression. The overall response was a partial response. Therefore, crizotinib exists an attractive therapeutic option for patients with SRCA. However, in the present study, acquired drug resistance to crizotinib developed after only one month of treatment. It would consequently be valuable to investigate the mechanisms underlying acquired crizotinib resistance in future studies.
Keywords: EML4-ALK; crizotinib; primary signet-ring cell adenocarcinoma.
Figures


References
-
- Shaw AT, Yeap BY, Mino-Kenudson M, Digumarthy SR, Costa DB, Heist RS, Solomon B, Stubbs H, Admane S, McDermott U, Settleman J, Kobayashi S, Mark EJ, Rodig SJ, Chirieac LR, Kwak EL, Lynch TJ, Iafrate AJ. Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who harbor EML4-ALK. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4247–4253. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.6993. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rodig SJ, Mino-Kenudson M, Dacic S, Yeap BY, Shaw A, Barletta JA, Stubbs H, Law K, Lindeman N, Mark E, Janne PA, Lynch T, Johnson BE, Iafrate AJ, Chirieac LR. Unique clinicopathologic features characterize ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma in the western population. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:5216–5223. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0802. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
