Histone Deacetylases Inhibitors in the Treatment of Retinal Degenerative Diseases: Overview and Perspectives
- PMID: 26137316
- PMCID: PMC4468288
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/250812
Histone Deacetylases Inhibitors in the Treatment of Retinal Degenerative Diseases: Overview and Perspectives
Abstract
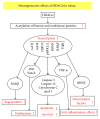
Retinal degenerative diseases are one of the important refractory ophthalmic diseases, featured with apoptosis of photoreceptor cells. Histone acetylation and deacetylation can regulate chromosome assembly, gene transcription, and posttranslational modification, which are regulated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs), respectively. The histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) have the ability to cause hyperacetylation of histone and nonhistone proteins, resulting in a variety of effects on cell proliferation, differentiation, anti-inflammation, and anti-apoptosis. Several HDACis have been approved for clinical trials to treat cancer. Studies have shown that HDACis have neuroprotective effects in nervous system damage. In this paper, we will summarize the neuroprotective effects of common HDACis in retinal degenerative diseases and make a prospect to the applications of HDACis in the treatment of retinal degenerative diseases in the future.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

