Dengue subgenomic RNA binds TRIM25 to inhibit interferon expression for epidemiological fitness
- PMID: 26138103
- PMCID: PMC4824004
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aab3369
Dengue subgenomic RNA binds TRIM25 to inhibit interferon expression for epidemiological fitness
Abstract
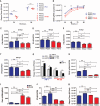
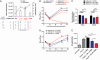
The global spread of dengue virus (DENV) infections has increased viral genetic diversity, some of which appears associated with greater epidemic potential. The mechanisms governing viral fitness in epidemiological settings, however, remain poorly defined. We identified a determinant of fitness in a foreign dominant (PR-2B) DENV serotype 2 (DENV-2) clade, which emerged during the 1994 epidemic in Puerto Rico and replaced an endemic (PR-1) DENV-2 clade. The PR-2B DENV-2 produced increased levels of subgenomic flavivirus RNA (sfRNA) relative to genomic RNA during replication. PR-2B sfRNA showed sequence-dependent binding to and prevention of tripartite motif 25 (TRIM25) deubiquitylation, which is critical for sustained and amplified retinoic acid-inducible gene 1 (RIG-I)-induced type I interferon expression. Our findings demonstrate a distinctive viral RNA-host protein interaction to evade the innate immune response for increased epidemiological fitness.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

Comment in
-
Dengue Non-coding RNA: TRIMmed for Transmission.Cell Host Microbe. 2015 Aug 12;18(2):133-4. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.07.009. Cell Host Microbe. 2015. PMID: 26269946
References
-
- Bennett SN, et al. J. Gen. Virol. 2006;87:885–893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

