The center for causal discovery of biomedical knowledge from big data
- PMID: 26138794
- PMCID: PMC5009908
- DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocv059
The center for causal discovery of biomedical knowledge from big data
Erratum in
-
Correction.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2023 Dec 22;31(1):281. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocad155. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37757460 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
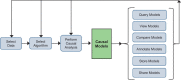
The Big Data to Knowledge (BD2K) Center for Causal Discovery is developing and disseminating an integrated set of open source tools that support causal modeling and discovery of biomedical knowledge from large and complex biomedical datasets. The Center integrates teams of biomedical and data scientists focused on the refinement of existing and the development of new constraint-based and Bayesian algorithms based on causal Bayesian networks, the optimization of software for efficient operation in a supercomputing environment, and the testing of algorithms and software developed using real data from 3 representative driving biomedical projects: cancer driver mutations, lung disease, and the functional connectome of the human brain. Associated training activities provide both biomedical and data scientists with the knowledge and skills needed to apply and extend these tools. Collaborative activities with the BD2K Consortium further advance causal discovery tools and integrate tools and resources developed by other centers.
Keywords: Big Data to knowledge (BD2K); biomedical knowledge; biomedical science; causal discovery; center of excellence.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association.All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Glymour C, Cooper GF, eds. Computation, Causation, and Discovery. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 1999.
-
- Spirtes P, Glymour C, Scheines R. Causation, Prediction, and Search. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2000.
-
- Pearl J. Causality: Models, Reasoning, and Inference. Cambridge, U.K: Cambridge University Press; 2009.
-
- Spirtes P. Introduction to causal inference. J Mach Learn Res. 2010;11:1643-1662.
-
- Illari PM, Russo F, Williamson J, eds. Causality in the Sciences. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

