Obesity-induced DNA hypermethylation of the adiponectin gene mediates insulin resistance
- PMID: 26139044
- PMCID: PMC4506505
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8585
Obesity-induced DNA hypermethylation of the adiponectin gene mediates insulin resistance
Abstract
Adiponectin plays a key role in the regulation of the whole-body energy homeostasis by modulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Although obesity-induced reduction of adiponectin expression is primarily ascribed to a transcriptional regulation failure, the underlying mechanisms are largely undefined. Here we show that DNA hypermethylation of a particular region of the adiponectin promoter suppresses adiponectin expression through epigenetic control and, in turn, exacerbates metabolic diseases in obesity. Obesity-induced, pro-inflammatory cytokines promote DNMT1 expression and its enzymatic activity. Activated DNMT1 selectively methylates and stimulates compact chromatin structure in the adiponectin promoter, impeding adiponectin expression. Suppressing DNMT1 activity with a DNMT inhibitor resulted in the amelioration of obesity-induced glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in an adiponectin-dependent manner. These findings suggest a critical role of adiponectin gene epigenetic control by DNMT1 in governing energy homeostasis, implying that modulating DNMT1 activity represents a new strategy for the treatment of obesity-related diseases.
Figures

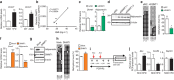

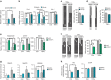




Comment in
-
Epigenetics: Obesity-induced hypermethylation of adiponectin gene.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015 Sep;11(9):504. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.116. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26170023 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jaenisch R. & Bird A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat. Genet. 33, (Suppl) 245–254 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Barres R. et al. Non-CpG methylation of the PGC-1alpha promoter through DNMT3B controls mitochondrial density. Cell Metab. 10, 189–198 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

