An Interglomerular Circuit Gates Glomerular Output and Implements Gain Control in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb
- PMID: 26139373
- PMCID: PMC4633092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.06.019
An Interglomerular Circuit Gates Glomerular Output and Implements Gain Control in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb
Abstract
Odors elicit distributed activation of glomeruli in the olfactory bulb (OB). Crosstalk between co-active glomeruli has been proposed to perform a variety of computations, facilitating efficient extraction of sensory information by the cortex. Dopaminergic/GABAergic cells in the OB, which can be identified by their expression of the dopamine transporter (DAT), provide the earliest opportunity for such crosstalk. Here we show in mice that DAT+ cells carry concentration-dependent odor signals and broadcast focal glomerular inputs throughout the OB to cause suppression of mitral/tufted (M/T) cell firing, an effect that is mediated by the external tufted (ET) cells coupled to DAT+ cells via chemical and electrical synapses. We find that DAT+ cells implement gain control and decorrelate odor representations in the M/T cell population. Our results further indicate that ET cells are gatekeepers of glomerular output and prime determinants of M/T responsiveness.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
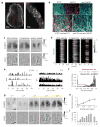

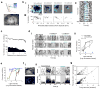



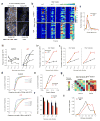

References
-
- Aungst JL, Heyward PM, Puche AC, Karnup SV, Hayar A, Szabo G, Shipley MT. Centre-surround inhibition among olfactory bulb glomeruli. Nature. 2003;426:623–629. - PubMed
-
- Barlow Horace. In: Possible principles underlying the transformation of sensory messages. Rosenblith WA, editor. MIT Press; Cambridge, MA: 1961.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

