Pulmonary edema following transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect
- PMID: 26139760
- PMCID: PMC4881711
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-9784.159827
Pulmonary edema following transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect
Abstract
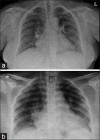
We describe an incident of development of acute pulmonary edema after the device closure of a secundum atrial septal defect in a 52-year-old lady, which was treated with inotropes, diuretics and artificial ventilation. Possibility of acute left ventricular dysfunction should be considered after the defect closure in the middle-aged patients as the left ventricular compliance may be reduced due to increased elastic stiffness and diastolic dysfunction. Baseline left atrial pressure may be > 10 mmHg in these patients. Associated risk factors for the left ventricular dysfunction are a large Qp:Qs ratio, systemic hypertension, severe pulmonary hypertension and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Knirsch W, Dodge-Khatami A, Valsangiacomo-Buechel E, Weiss M, Berger F. Challenges encountered during closure of atrial septal defects. Pediatr Cardiol. 2005;26:147–53. - PubMed
-
- Masutani S, Senzaki H. Left ventricular function in adult patients with atrial septal defect: Implication for development of heart failure after transcatheter closure. J Card Fail. 2011;17:957–63. - PubMed
-
- Satoh A, Katayama K, Hiro T, Yano M, Miura T, Kohno M, et al. Effect of right ventricular volume overload on left ventricular diastolic function in patients with atrial septal defect. Jpn Circ J. 1996;60:758–66. - PubMed
-
- Gruner C, Akkaya E, Kretschmar O, Roffi M, Corti R, Jenni R, et al. Pharmacologic preconditioning therapy prior to atrial septal defect closure in patients at high risk for acute pulmonary edema. J Interv Cardiol. 2012;25:505–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical