Intranuclear Actin Regulates Osteogenesis
- PMID: 26140478
- PMCID: PMC4788101
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.2090
Intranuclear Actin Regulates Osteogenesis
Abstract
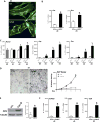
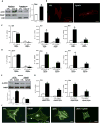
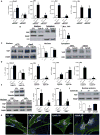
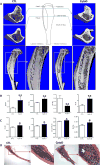
Depolymerization of the actin cytoskeleton induces nuclear trafficking of regulatory proteins and global effects on gene transcription. We here show that in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), cytochalasin D treatment causes rapid cofilin-/importin-9-dependent transfer of G-actin into the nucleus. The continued presence of intranuclear actin, which forms rod-like structures that stain with phalloidin, is associated with induction of robust expression of the osteogenic genes osterix and osteocalcin in a Runx2-dependent manner, and leads to acquisition of osteogenic phenotype. Adipogenic differentiation also occurs, but to a lesser degree. Intranuclear actin leads to nuclear export of Yes-associated protein (YAP); maintenance of nuclear YAP inhibits Runx2 initiation of osteogenesis. Injection of cytochalasin into the tibial marrow space of live mice results in abundant bone formation within the space of 1 week. In sum, increased intranuclear actin forces MSC into osteogenic lineage through controlling Runx2 activity; this process may be useful for clinical objectives of forming bone.
Keywords: Bone; Cofilin; Cytoskeleton; Importin 9; Mesenchymal stem cells; Runx2; Yes-associated protein.
© 2015 AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intranuclear Actin Structure Modulates Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation.Stem Cells. 2017 Jun;35(6):1624-1635. doi: 10.1002/stem.2617. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Stem Cells. 2017. PMID: 28371128 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the integrin αVβ3- actin filaments axis in early osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells under cyclic tensile stress.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Oct 30;21(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-01027-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37904190 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of formin mDia2 alters lamin B1 levels and increases osteogenesis in stem cells.Stem Cells. 2020 Jan;38(1):102-117. doi: 10.1002/stem.3098. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 31648392 Free PMC article.
-
As functional nuclear actin comes into view, is it globular, filamentous, or both?J Cell Biol. 2008 Mar 24;180(6):1061-4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200709082. Epub 2008 Mar 17. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18347069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A light way for nuclear cell biologists.J Biochem. 2021 Apr 18;169(3):273-286. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvaa139. J Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33245128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exercise Increases and Browns Muscle Lipid in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016 Jun 30;7:80. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00080. eCollection 2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016. PMID: 27445983 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative proteomic analysis of human mesenchymal stromal cell behavior on calcium phosphate ceramics with different osteoinductive potential.Mater Today Bio. 2020 Jun 24;7:100066. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2020.100066. eCollection 2020 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2020. PMID: 32642640 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cofilin in age-related neuroinflammation.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Aug;15(8):1451-1459. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.274330. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31997804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concise Review: Plasma and Nuclear Membranes Convey Mechanical Information to Regulate Mesenchymal Stem Cell Lineage.Stem Cells. 2016 Jun;34(6):1455-63. doi: 10.1002/stem.2342. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Stem Cells. 2016. PMID: 26891206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear actin is a critical regulator of Drosophila female germline stem cell maintenance.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 28:2024.08.27.609996. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.27.609996. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39253513 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

