Fonsecaea pedrosoi-induced Th17-cell differentiation in mice is fostered by Dectin-2 and suppressed by Mincle recognition
- PMID: 26140582
- PMCID: PMC4562893
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201545591
Fonsecaea pedrosoi-induced Th17-cell differentiation in mice is fostered by Dectin-2 and suppressed by Mincle recognition
Abstract
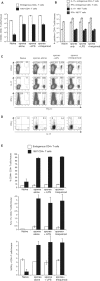
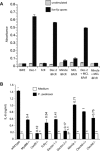
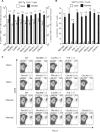
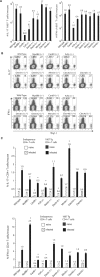
Chromoblastomycosis is a chronic skin infection caused by the pigmented saprophytic mould Fonsecaea pedrosoi. Chronicity of infection can be broken by a coordinated innate recognition of the spores by pattern recognition receptors. While Mincle signaling via the Syk/Card9 pathway is required for fungal recognition by host cells, it is not sufficient for host control. Exogenously applied TLR agonists are necessary to promote the induction of proinflammatory cytokines and clearance of infection in vivo. Here, we investigated whether costimulation by TLR agonists fosters the development of adaptive immune responses, by examining the development of fungus-specific T cells. Subcutaneous infection of mice with F. pedrosoi spores induced the activation, expansion, and differentiation of Ag-specific CD4(+) T cells but TLR costimulation did not further augment these T-cell responses. The Dectin-2/FcRγ/Card9 signaling pathway promoted the differentiation of fungus-specific CD4(+) T cells into Th17 cells, whereas Mincle inhibited the development of this T-helper subset in infected mice. These results indicate differential roles for Dectin-2 and Mincle in the generation of adaptive immune responses to F. pedrosoi infection.
Keywords: C-type lectin; Chromoblastomycosis; Dectin-2; Fungi; Mincle; T-cell differentiation; Th17 cell.
© 2015 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
References
-
- Queiroz‐Telles, F. , Esterre, P. , Perez‐Blanco, M. , Vitale, R. G. , Salgado, C. G. and Bonifaz, A. , Chromoblastomycosis: an overview of clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment. Med. Mycol. 2009. 47: 3–15. - PubMed
-
- Ameen, M. , Chromoblastomycosis: clinical presentation and management. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2009. 34: 849–854. - PubMed
-
- Santos, A. L. , Palmeira, V. F. , Rozental, S. , Kneipp, L. F. , Nimrichter, L. , Alviano, D. S. , Rodrigues, M. L. and Alviano, C. S. , Biology and pathogenesis of Fonsecaea pedrosoi, the major etiologic agent of chromoblastomycosis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2007. 31: 570–591. - PubMed
-
- Brandt, M. E. and Warnock, D. W. , Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and therapy of infections caused by dematiaceous fungi. J. Chemother. 2003. 15 (Suppl 2): 36–47. - PubMed
-
- Ricard‐Blum, S. , Hartmann, D. J. and Esterre, P. , Monitoring of extracellular matrix metabolism and cross‐linking in tissue, serum and urine of patients with chromoblastomycosis, a chronic skin fibrosis. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 1998. 28: 748–754. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

