Topological characterization of neuronal arbor morphology via sequence representation: II--global alignment
- PMID: 26141505
- PMCID: PMC4491275
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-015-0605-1
Topological characterization of neuronal arbor morphology via sequence representation: II--global alignment
Abstract
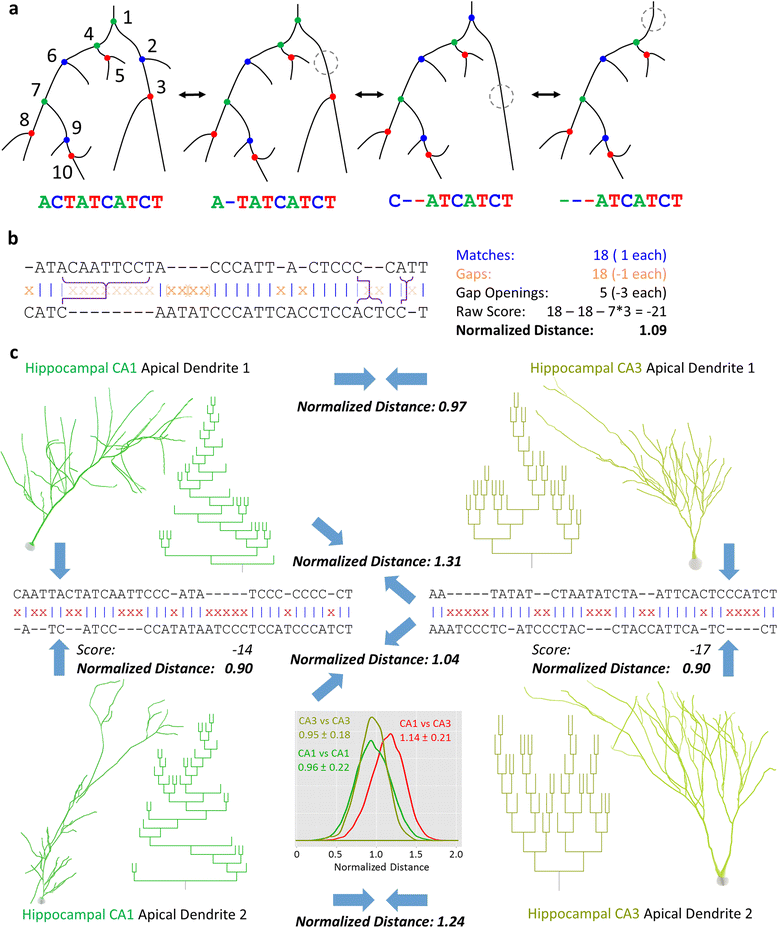
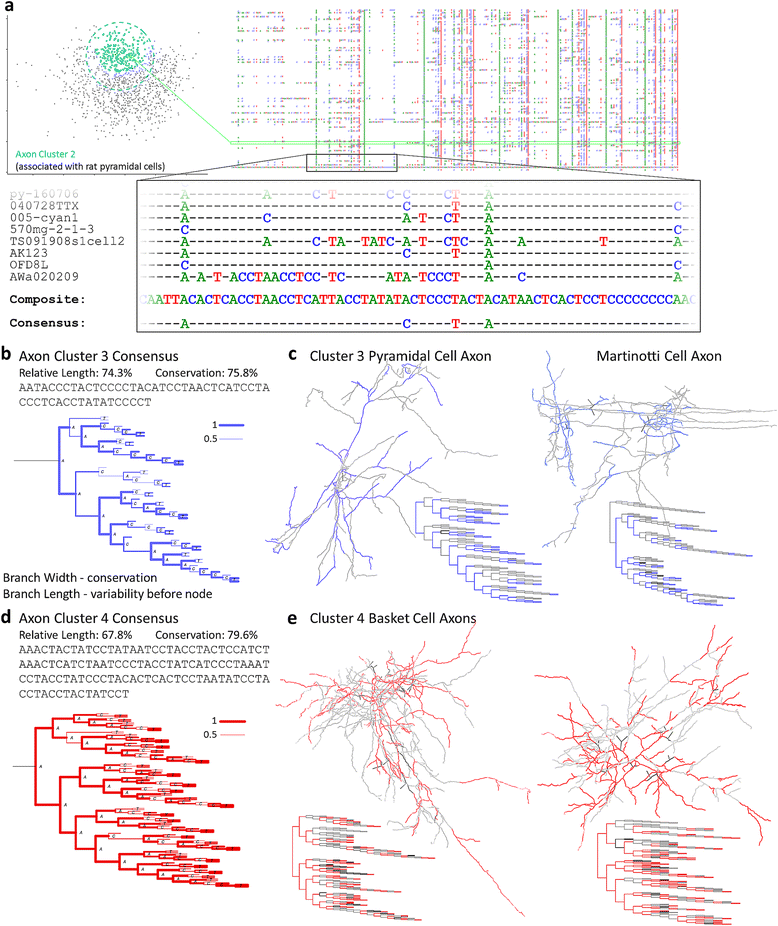
Background: The increasing abundance of neuromorphological data provides both the opportunity and the challenge to compare massive numbers of neurons from a wide diversity of sources efficiently and effectively. We implemented a modified global alignment algorithm representing axonal and dendritic bifurcations as strings of characters. Sequence alignment quantifies neuronal similarity by identifying branch-level correspondences between trees.
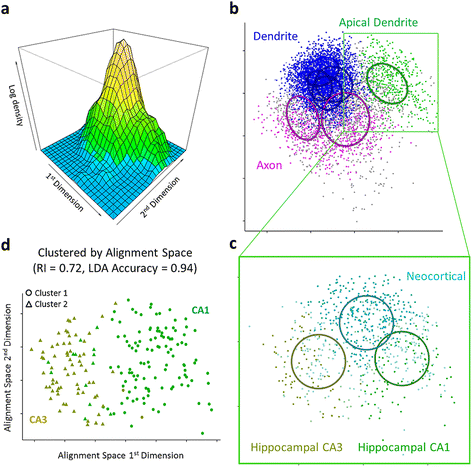
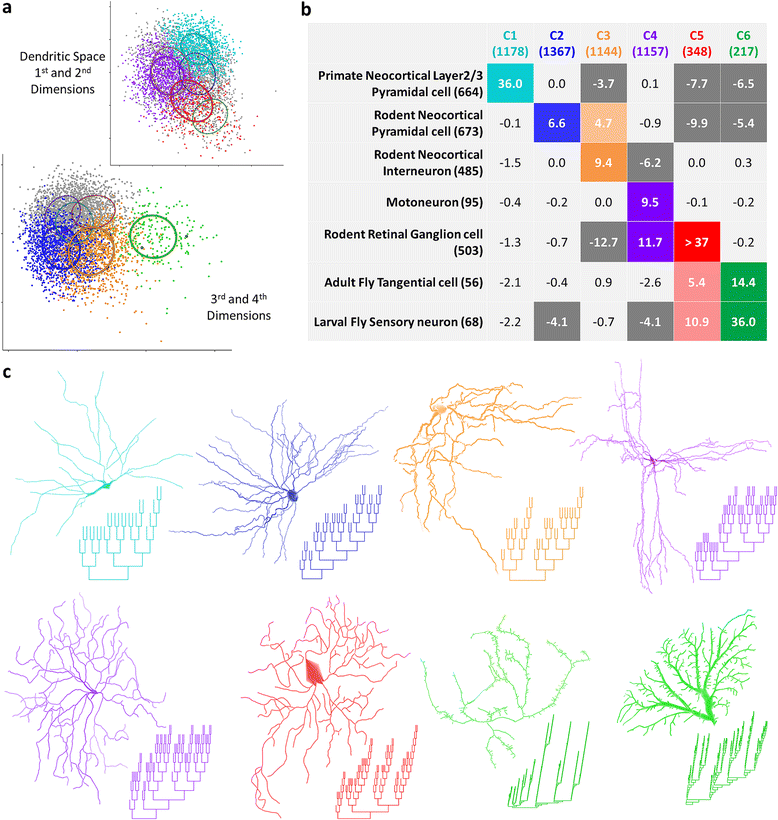
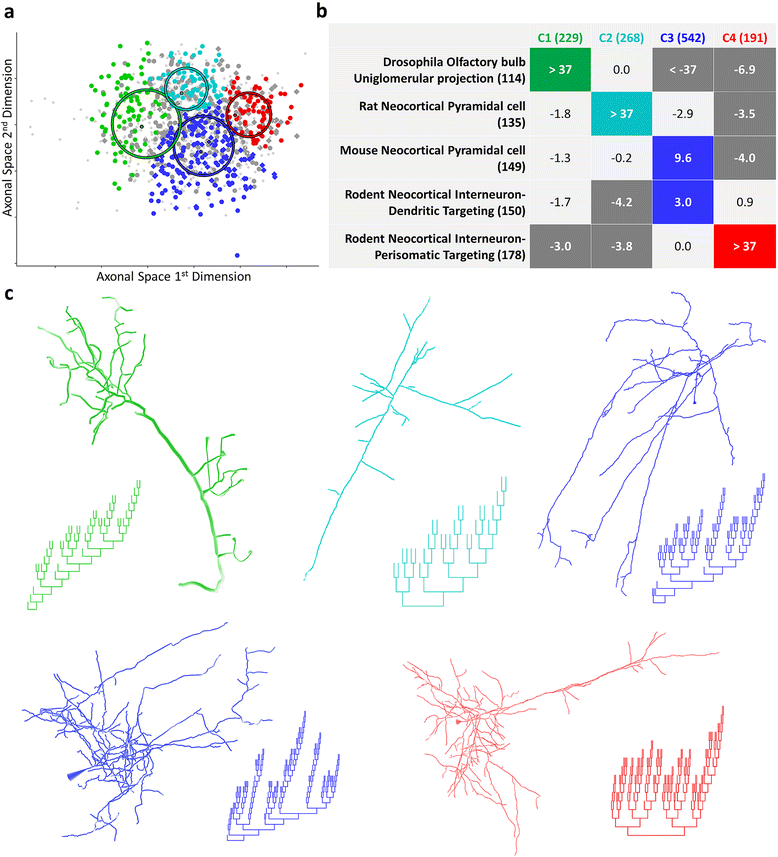
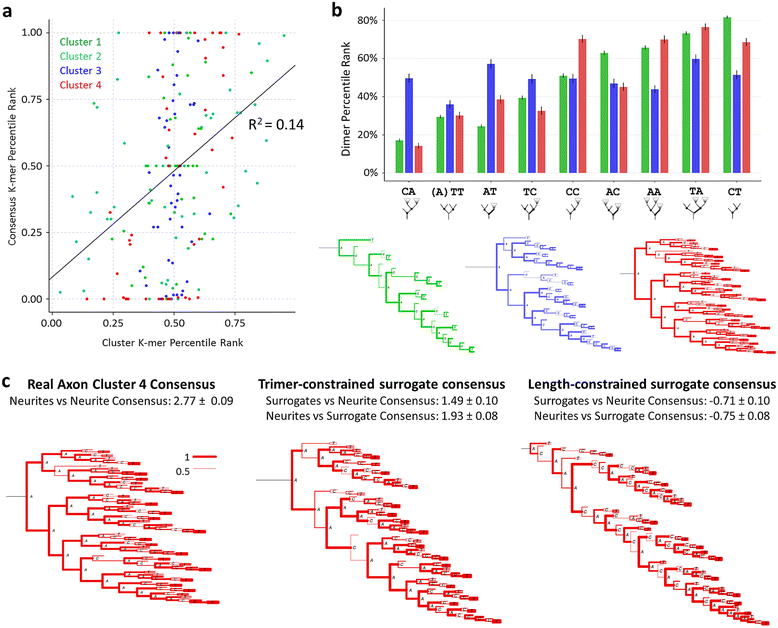
Results: The space generated from pairwise similarities is capable of classifying neuronal arbor types as well as, or better than, traditional topological metrics. Unsupervised cluster analysis produces groups that significantly correspond with known cell classes for axons, dendrites, and pyramidal apical dendrites. Furthermore, the distinguishing consensus topology generated by multiple sequence alignment of a group of neurons reveals their shared branching blueprint. Interestingly, the axons of dendritic-targeting interneurons in the rodent cortex associates with pyramidal axons but apart from the (more topologically symmetric) axons of perisomatic-targeting interneurons.
Conclusions: Global pairwise and multiple sequence alignment of neurite topologies enables detailed comparison of neurites and identification of conserved topological features in alignment-defined clusters. The methods presented also provide a framework for incorporation of additional branch-level morphological features. Moreover, comparison of multiple alignment with motif analysis shows that the two techniques provide complementary information respectively revealing global and local features.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Topological characterization of neuronal arbor morphology via sequence representation: I--motif analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Jul 10;16:216. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0604-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26156313 Free PMC article.
-
Growing dendrites and axons differ in their reliance on the secretory pathway.Cell. 2007 Aug 24;130(4):717-29. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.032. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17719548 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological Characterization of a Cortico-cortical relay in the cat sensorimotor cortex.Cereb Cortex. 1997 Mar;7(2):100-9. doi: 10.1093/cercor/7.2.100. Cereb Cortex. 1997. PMID: 9087819
-
Neuronal polarity and trafficking.Neuron. 2003 Oct 9;40(2):277-95. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00629-9. Neuron. 2003. PMID: 14556709 Review.
-
Homology assessment and molecular sequence alignment.J Biomed Inform. 2006 Feb;39(1):18-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2005.11.005. Epub 2005 Dec 9. J Biomed Inform. 2006. PMID: 16380300 Review.
Cited by
-
Topological characterization of neuronal arbor morphology via sequence representation: I--motif analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Jul 10;16:216. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0604-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26156313 Free PMC article.
-
DSM: Deep sequential model for complete neuronal morphology representation and feature extraction.Patterns (N Y). 2023 Dec 13;5(1):100896. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100896. eCollection 2024 Jan 12. Patterns (N Y). 2023. PMID: 38264721 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Evaluation of Interneuron Morphology Representations for Cell Type Discrimination.Neuroinformatics. 2020 Oct;18(4):591-609. doi: 10.1007/s12021-020-09461-z. Neuroinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32367332 Free PMC article.
-
Large scale similarity search across digital reconstructions of neural morphology.Neurosci Res. 2022 Aug;181:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2022.05.004. Epub 2022 May 14. Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 35580795 Free PMC article.
-
BlastNeuron for Automated Comparison, Retrieval and Clustering of 3D Neuron Morphologies.Neuroinformatics. 2015 Oct;13(4):487-99. doi: 10.1007/s12021-015-9272-7. Neuroinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26036213
References
-
- Ascoli GA, Donohue DE, Halavi M. NeuroMorpho.Org: a central resource for neuronal morphologies. J Neurosci. 2007;27:9247–51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2055-07.2007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

