CDK1-Mediated SIRT3 Activation Enhances Mitochondrial Function and Tumor Radioresistance
- PMID: 26141949
- PMCID: PMC4560959
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0017
CDK1-Mediated SIRT3 Activation Enhances Mitochondrial Function and Tumor Radioresistance
Abstract
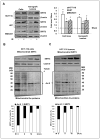
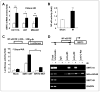
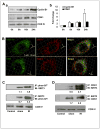
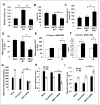
Tumor adaptive resistance to therapeutic radiation remains a barrier for further improvement of local cancer control. SIRT3, a member of the sirtuin family of NAD(+)-dependent protein deacetylases in mitochondria, promotes metabolic homeostasis through regulation of mitochondrial protein deacetylation and plays a key role in prevention of cell aging. Here, we demonstrate that SIRT3 expression is induced in an array of radiation-treated human tumor cells and their corresponding xenograft tumors, including colon cancer HCT-116, glioblastoma U87, and breast cancer MDA-MB231 cells. SIRT3 transcriptional activation is due to SIRT3 promoter activation controlled by the stress transcription factor NF-κB. Posttranscriptionally, SIRT3 enzymatic activity is further enhanced via Thr150/Ser159 phosphorylation by cyclin B1-CDK1, which is also induced by radiation and relocated to mitochondria together with SIRT3. Cells expressing Thr150Ala/Ser159Ala-mutant SIRT3 show a reduction in mitochondrial protein lysine deacetylation, Δψm, MnSOD activity, and mitochondrial ATP generation. The clonogenicity of Thr150Ala/Ser159Ala-mutant transfectants is lower and significantly decreased under radiation. Tumors harboring Thr150Ala/Ser159Ala-mutant SIRT3 show inhibited growth and increased sensitivity to in vivo local irradiation. These results demonstrate that enhanced SIRT3 transcription and posttranslational modifications in mitochondria contribute to adaptive radioresistance in tumor cells. CDK1-mediated SIRT3 phosphorylation is a potential effective target to sensitize tumor cells to radiotherapy.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflicts.
Figures


References
-
- Recht A, Come SE, Henderson IC, Gelman RS, Silver B, Hayes DF, et al. The sequencing of chemotherapy and radiation therapy after conservative surgery for early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1356–61. - PubMed
-
- Auperin A, Le Pechoux C, Rolland E, Curran WJ, Furuse K, Fournel P, et al. Meta-analysis of concomitant versus sequential radiochemotherapy in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2181–90. - PubMed
-
- Peters LJ, O’Sullivan B, Giralt J, Fitzgerald TJ, Trotti A, Bernier J, et al. Critical impact of radiotherapy protocol compliance and quality in the treatment of advanced head and neck cancer: results from TROG 02.02. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2996–3001. - PubMed
-
- Liang K, Lu Y, Jin W, Ang KK, Milas L, Fan Z. Sensitization of breast cancer cells to radiation by trastuzumab. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:1113–20. - PubMed
-
- Debeb BG, Xu W, Woodward WA. Radiation resistance of breast cancer stem cells: understanding the clinical framework. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2009;14:11–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

