Removal of H2A.Z by INO80 promotes homologous recombination
- PMID: 26142279
- PMCID: PMC4552491
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.201540330
Removal of H2A.Z by INO80 promotes homologous recombination
Abstract
The mammalian INO80 remodelling complex facilitates homologous recombination (HR), but the mechanism by which it does this is unclear. Budding yeast INO80 can remove H2A.Z/H2B dimers from chromatin and replace them with H2A/H2B dimers. H2A.Z is actively incorporated at sites of damage in mammalian cells, raising the possibility that H2A.Z may need to be subsequently removed for resolution of repair. Here, we show that H2A.Z in human cells is indeed rapidly removed from chromatin flanking DNA damage by INO80. We also report that the histone chaperone ANP32E, which is implicated in removing H2AZ from chromatin, similarly promotes HR and appears to work on the same pathway as INO80 in these assays. Importantly, we demonstrate that the HR defect in cells depleted of INO80 or ANP32E can be rescued by H2A.Z co-depletion, suggesting that H2A.Z removal from chromatin is the primary function of INO80 and ANP32E in promoting homologous recombination.
Keywords: ANP32E; H2A.Z; INO80; chromatin; homologous recombination.
© 2015 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Figures

A, B U2OS cells transfected with GFP-tagged H2B (A) or EGFP-tagged RuvBL2 (B) were laser micro-irradiated and monitored by live cell imaging. Representative images taken at indicated time points are shown.
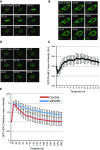
H2A.Z is rapidly incorporated and removed from chromatin in the vicinity of damaged DNA. U2OS cells transfected with GFP-H2A.Z were laser micro-irradiated and monitored by live cell imaging. Representative images taken at indicated time points are shown.
The RuvBL2 subunit of INO80 accumulates at sites of damaged DNA. U2OS cells transfected with EGFP-RuvBL2 were laser micro-irradiated and monitored by live cell imaging. Representative images taken at indicated time points are shown.
Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity at sites of micro-irradiation ± SE (n = 3).
Removal of H2A.Z from chromatin in the vicinity of damaged DNA is at least partly dependent on INO80. USOS cells treated with siINO80 were transfected with GFP-H2A.Z, laser micro-irradiated and monitored by live cell imaging. Representative images taken at indicated time points are shown.
Quantification of relative mean fluorescence intensity ± SD at sites of micro-irradiation in control (U2OS; n = 3) and siINO80 cells (n = 3) in a minimum of 10 cells per experiment.
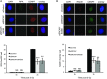
IR induced RPA focus formation in A549 cells treated with siControl, siSRCAP or siSRCAP/siINO80. Upper panel: representative images. Lower panel: quantification of foci. When compared with control cells at 2 h, siSRCAP and siSRCAP/siINO80 are significantly different (***P = 0.0009 and **P = 0.002, respectively).
IR induced RAD51 focus formation in cells as in (A). Upper panel: representative images. Lower panel: quantification of foci as in (A). When compared with control cells at 2 h, siSRCAP and siSRCAP/siINO80 are significantly different (***P = 0.00098 and **P = 0.00248, respectively).
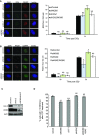
IR induced RPA focus formation in A549 cells treated with siControl, siINO80, siH2A.Z or siINO80/siH2A.Z. Left hand panel: representative images. Right hand panel: quantification of foci.
IR induced RAD51 focus formation in A549 cells treated with siControl, siINO80, siH2A.Z or siINO80/siH2A.Z. Left hand panel: representative images. Right hand panel: quantification of foci.
Western blot analysis showing efficiency of siRNA depletion. KAP1 is used as a loading control.
Quanitification of RPA foci following 1 h of treatment with camptothecin (CPT).
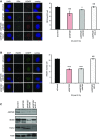
IR induced RPA focus formation in A549 cells treated with siControl, siANP32E, siANP32E/siINO80 or siANP32E/siH2A.Z. Left hand panel: representative images. Right hand panel: mean number of foci ± SD.
IR induced RAD51 focus formation in A549 cells treated with siControl, siANP32E, siANP32E/siINO80 or siANP32E/siH2A.Z. Left hand panel: representative images. Right hand panel: mean number of foci ± SD.
Western blot analysis showing efficiency of siRNA depletion. Ku80 is used as a loading control.
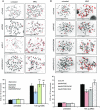
SCEs were monitored in HeLa cells treated with siControl, siINO80, siH2A.Z or siINO80/siH2A.Z following treatment with mitomycin C (MMC). The reduction in SCEs in cells lacking INO80 is rescued by the co-depletion of H2A.Z. Upper panel: representative images. Lower panel: mean number of SCEs ± SD. SCEs were scored in at least 1,000 chromosomes from three independent experiments.
SCEs were monitored in HeLa cells treated with siControl, siANP32E, siANP32E/siINO80 or siANP32E/siH2A.Z. There is no further reduction in SCEs in cells depleted of both ANP32E and INO80 when compared with ANP32E alone. As with siINO80, the reduction in SCEs in cells lacking ANP32E can be rescued by the co-depletion of H2A.Z. Upper panel: representative images. Lower panel: mean number of foci ± SD.
References
-
- Watanabe S, Peterson CL. The INO80 family of chromatin-remodeling enzymes: regulators of histone variant dynamics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010;75:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Mizuguchi G, Shen X, Landry J, Wu WH, Sen S, Wu C. ATP-driven exchange of histone H2AZ variant catalyzed by SWR1 chromatin remodeling complex. Science. 2004;303:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Ruhl DD, Jin J, Cai Y, Swanson S, Florens L, Washburn MP, Conaway RC, Conaway JW, Chrivia JC. Purification of a human SRCAP complex that remodels chromatin by incorporating the histone variant H2A.Z into nucleosomes. Biochemistry. 2006;45:5671–5677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

