MDN: A Web Portal for Network Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulations
- PMID: 26143656
- PMCID: PMC4576149
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.013
MDN: A Web Portal for Network Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Erratum in
- Biophys J. 2015 Oct 6;109(7):1509
Abstract
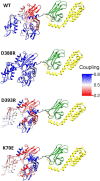
We introduce a web portal that employs network theory for the analysis of trajectories from molecular dynamics simulations. Users can create protein energy networks following methodology previously introduced by our group, and can identify residues that are important for signal propagation, as well as measure the efficiency of signal propagation by calculating the network coupling. This tool, called MDN, was used to characterize signal propagation in Escherichia coli heat-shock protein 70-kDa. Two variants of this protein experimentally shown to be allosterically active exhibit higher network coupling relative to that of two inactive variants. In addition, calculations of partial coupling suggest that this quantity could be used as part of the criteria to determine pocket druggability in drug discovery studies.
Copyright © 2015 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Lindahl E. Molecular Modeling of Proteins. Springer; New York: 2015. Molecular dynamics simulations; pp. 3–26.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

