A Strategic Study about Quality Characteristics in e-Health Systems Based on a Systematic Literature Review
- PMID: 26146656
- PMCID: PMC4471398
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/863591
A Strategic Study about Quality Characteristics in e-Health Systems Based on a Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
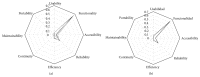
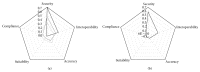
e-Health Systems quality management is an expensive and hard process that entails performing several tasks such as analysis, evaluation, and quality control. Furthermore, the development of an e-Health System involves great responsibility since people's health and quality of life depend on the system and services offered. The focus of the following study is to identify the gap in Quality Characteristics for e-Health Systems, by detecting not only which are the most studied, but also which are the most used Quality Characteristics these Systems include. A strategic study is driven in this paper by a Systematic Literature Review so as to identify Quality Characteristics in e-Health. Such study makes information and communication technology organizations reflect and act strategically to manage quality in e-Health Systems efficiently and effectively. As a result, this paper proposes the bases of a Quality Model and focuses on a set of Quality Characteristics to enable e-Health Systems quality management. Thus, we can conclude that this paper contributes to implementing knowledge with regard to the mission and view of e-Health (Systems) quality management and helps understand how current researches evaluate quality in e-Health Systems.
Figures
References
-
- Goletsis Y., Chletsos M. Towards a unified methodology for the evaluation of e-health applications. Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine (ITAB '10); November 2010; pp. 1–4. - DOI
-
- Mettler T., Vimarlund V. Evaluation of e-health strategies: a portfolio approach. Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Health Information Management Research; 2011; pp. 296–305.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous