Analysis of a Multi-component Multi-stage Malaria Vaccine Candidate--Tackling the Cocktail Challenge
- PMID: 26147206
- PMCID: PMC4492585
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131456
Analysis of a Multi-component Multi-stage Malaria Vaccine Candidate--Tackling the Cocktail Challenge
Abstract
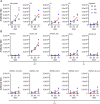
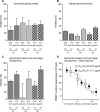
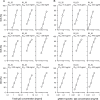
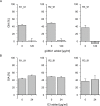
Combining key antigens from the different stages of the P. falciparum life cycle in the context of a multi-stage-specific cocktail offers a promising approach towards the development of a malaria vaccine ideally capable of preventing initial infection, the clinical manifestation as well as the transmission of the disease. To investigate the potential of such an approach we combined proteins and domains (11 in total) from the pre-erythrocytic, blood and sexual stages of P. falciparum into a cocktail of four different components recombinantly produced in plants. After immunization of rabbits we determined the domain-specific antibody titers as well as component-specific antibody concentrations and correlated them with stage specific in vitro efficacy. Using purified rabbit immune IgG we observed strong inhibition in functional in vitro assays addressing the pre-erythrocytic (up to 80%), blood (up to 90%) and sexual parasite stages (100%). Based on the component-specific antibody concentrations we calculated the IC50 values for the pre-erythrocytic stage (17-25 μg/ml), the blood stage (40-60 μg/ml) and the sexual stage (1.75 μg/ml). While the results underline the feasibility of a multi-stage vaccine cocktail, the analysis of component-specific efficacy indicates significant differences in IC50 requirements for stage-specific antibody concentrations providing valuable insights into this complex scenario and will thereby improve future approaches towards malaria vaccine cocktail development regarding the selection of suitable antigens and the ratios of components, to fine tune overall and stage-specific efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Organization WH. Ld Malaria Report 2012. World Health Organization. 2013;(1pp).
-
- Amador R, Moreno A, Murillo LA, Sierra O, Saavedra D, Rojas M, et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the Synthetic Malaria Vaccine Spf66 in a Large Field Trial. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1992;166(1):139–44. . - PubMed
-
- Doolan DL, Hoffman SL. DNA-based vaccines against malaria: status and promise of the Multi-Stage Malaria DNA Vaccine Operation. Int J Parasitol. 2001;31(8):753–62. . - PubMed
-
- Hill AVS, Reyes-Sandoval A, O'Hara G, Ewer K, Lawrie A, Goodman A, et al. Prime-boost vectored malaria vaccines Progress and prospects. Human vaccines. 2010;6(1):78–83. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

