Measurement of latent cognitive abilities involved in concept identification learning
- PMID: 26147832
- PMCID: PMC5104340
- DOI: 10.1080/13803395.2015.1042358
Measurement of latent cognitive abilities involved in concept identification learning
Abstract
Introduction: We used cognitive and psychometric modeling techniques to evaluate the construct validity and measurement precision of latent cognitive abilities measured by a test of concept identification learning: the Penn Conditional Exclusion Test (PCET).
Method: Item response theory parameters were embedded within classic associative- and hypothesis-based Markov learning models and were fitted to 35,553 Army soldiers' PCET data from the Army Study to Assess Risk and Resilience in Servicemembers (Army STARRS).
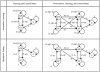
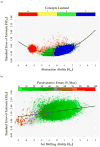
Results: Data were consistent with a hypothesis-testing model with multiple latent abilities-abstraction and set shifting. Latent abstraction ability was positively correlated with number of concepts learned, and latent set-shifting ability was negatively correlated with number of perseverative errors, supporting the construct validity of the two parameters. Abstraction was most precisely assessed for participants with abilities ranging from 1.5 standard deviations below the mean to the mean itself. Measurement of set shifting was acceptably precise only for participants making a high number of perseverative errors.
Conclusions: The PCET precisely measures latent abstraction ability in the Army STARRS sample, especially within the range of mildly impaired to average ability. This precision pattern is ideal for a test developed to measure cognitive impairment as opposed to cognitive strength. The PCET also measures latent set-shifting ability, but reliable assessment is limited to the impaired range of ability, reflecting that perseverative errors are rare among cognitively healthy adults. Integrating cognitive and psychometric models can provide information about construct validity and measurement precision within a single analytical framework.
Keywords: Army STARRS; Concept identification learning; Item response theory; Latent variable measurement; Neuropsychology; Penn Conditional Exclusion Test.
Figures

References
-
- Amos A. A computational model of information processing in the frontal cortex and basal ganglia. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2000;12:505–519. - PubMed
-
- Andersen EB. Estimating latent correlations between repeated testings. Psychometrika. 1985;50:3–16.
-
- Ashby F, Alfonso-Reese LA, Turken UU, Waldron EM. A neuropsychological theory of multiple systems in category learning. Psychological Review. 1998;105:442. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson RC, Bower GH, Crothers EJ. An introduction to mathematical learning theory. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons; 1965.
-
- Axelrod BN, Goldman RS, Heaton RK, Curtiss G, Thompson LL, Chelune GJ, Kay GG. Discriminability of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test using the standardization sample. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 1996;18:338–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
