Incidence and Geographic Distribution of Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa
- PMID: 26147963
- PMCID: PMC4493033
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132076
Incidence and Geographic Distribution of Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa
Abstract
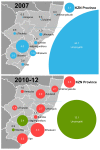
South Africa is experiencing a widespread drug-resistant tuberculosis epidemic, although data are limited regarding the current situation. This study finds that the extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) incidence in KwaZulu-Natal increased to 3.5 cases/100,000 (776 cases) in 2011-2012. XDR-TB cases are widely distributed geographically, with the majority of districts experiencing a rise in incidence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. (2013) Global Tuberculosis Report 2013. Geneva: The Organization; 2013. Report No.: Publication no. WHO/HTM/TB/2013.11.
-
- Shah N, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2006) Emergence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Extensive Resistant to Second-Line Drugs—Worldwide, 2000–2004. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 55:301–5. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi NR, Moll A, Sturm AW, Pawinski R, Govender T, Lalloo U, et al. (2006) Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis as a cause of death in patients co-infected with tuberculosis and HIV in a rural area of South Africa. Lancet. 368(9547):1575–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

