Interactome analysis brings splicing into focus
- PMID: 26149273
- PMCID: PMC4493805
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-015-0707-0
Interactome analysis brings splicing into focus
Abstract
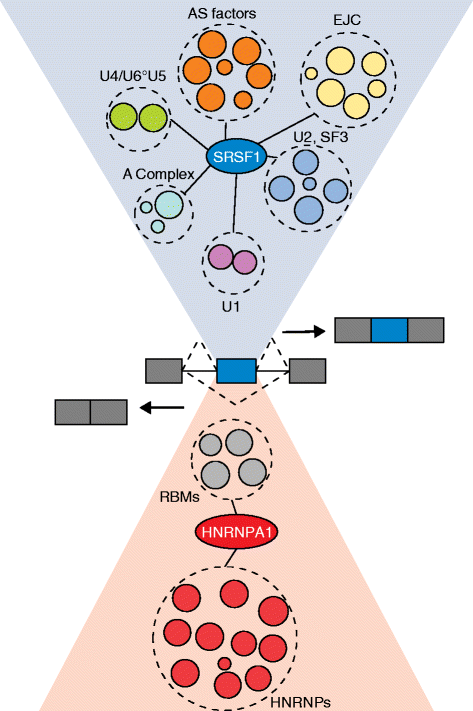
The spliceosome is a huge molecular machine that assembles dynamically onto its pre-mRNA substrates. A new study based on interactome analysis provides clues about how splicing-regulatory proteins modulate assembly of the spliceosome to either activate or repress splicing.Please see related Research article: http://www.genomebiology.com/2015/16/1/119/abstract.
Figures
Comment on
-
Differential connectivity of splicing activators and repressors to the human spliceosome.Genome Biol. 2015 Jun 6;16(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0682-5. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 26047612 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

