Function of a p24 Heterodimer in Morphogenesis and Protein Transport in Penicillium oxalicum
- PMID: 26149342
- PMCID: PMC4493713
- DOI: 10.1038/srep11875
Function of a p24 Heterodimer in Morphogenesis and Protein Transport in Penicillium oxalicum
Abstract
The lignocellulose degradation capacity of filamentous fungi has been widely studied because of their cellulase hypersecretion. The p24 proteins in eukaryotes serve important functions in this secretory pathway. However, little is known about the functions of the p24 proteins in filamentous fungi. In this study, four p24 proteins were identified in Penicillium oxalicum. Six p24 double-deletion strains were constructed, and further studies were carried out with the ΔerpΔpδ strain. The experimental results suggested that Erp and Pδ form a p24 heterodimer in vivo. This p24 heterodimer participates in important morphogenetic events, including sporulation, hyphal growth, and lateral branching. The results suggested that the p24 heterodimer mediates protein transport, particularly that of cellobiohydrolase. Analysis of the intracellular proteome revealed that the ΔerpΔpδ double mutant is under secretion stress due to attempts to remove proteins that are jammed in the endomembrane system. These results suggest that the p24 heterodimer participates in morphogenesis and protein transport. Compared with P. oxalicum Δerp, a greater number of cellular physiological pathways were impaired in ΔerpΔpδ. This finding may provide new insights into the secretory pathways of filamentous fungi.
Figures


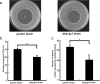
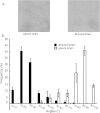
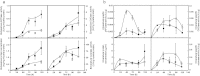
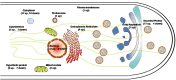
Similar articles
-
Early Secretory Pathway-Associated Proteins SsEmp24 and SsErv25 Are Involved in Morphogenesis and Pathogenicity in a Filamentous Phytopathogenic Fungus.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0317321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03173-21. Epub 2021 Dec 21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34933451 Free PMC article.
-
Functional diversity of the p24γ homologue Erp reveals physiological differences between two filamentous fungi.Fungal Genet Biol. 2013 Dec;61:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2013.08.017. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Fungal Genet Biol. 2013. PMID: 24035805
-
Linker length and flexibility induces new cellobiohydrolase activity of PoCel6A from Penicillium oxalicum.Biotechnol J. 2015 Jun;10(6):899-904. doi: 10.1002/biot.201400734. Epub 2015 May 5. Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25866282
-
Conidiation induction in Penicillium.Res Microbiol. 2003 Oct;154(8):539-46. doi: 10.1016/S0923-2508(03)00168-2. Res Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14527654 Review.
-
Control of morphogenesis in the human fungal pathogen Penicillium marneffei.Int J Med Microbiol. 2002 Oct;292(5-6):331-47. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00217. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12452280 Review.
Cited by
-
Early Secretory Pathway-Associated Proteins SsEmp24 and SsErv25 Are Involved in Morphogenesis and Pathogenicity in a Filamentous Phytopathogenic Fungus.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0317321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03173-21. Epub 2021 Dec 21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34933451 Free PMC article.
-
Gas-sensing riboceptors.RNA Biol. 2024 Jan;21(1):1-6. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2024.2379607. Epub 2024 Jul 17. RNA Biol. 2024. PMID: 39016047 Free PMC article.
-
ERV14 receptor impacts mycelial growth via its interactions with cell wall synthase and transporters in Aspergillus niger.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 11;14:1128462. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1128462. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37113235 Free PMC article.
-
Use of fusion transcription factors to reprogram cellulase transcription and enable efficient cellulase production in Trichoderma reesei.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 Oct 15;12:244. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1589-2. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 31636703 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Trichoderma reesei mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in cellulase formation.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017 Apr 20;10:99. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0789-x. eCollection 2017. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017. PMID: 28435444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lynd L. R. et al. How biotech can transform biofuels. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 169–172 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Liu G. D., Qin Y. Q., Li Z. H. & Qu Y. B. Improving lignocellulolytic enzyme production with Penicillium: from strains screening to systems biology. Biofuels 4, 523–534 (2013).
-
- Martinez D. et al. Genome sequencing and analysis of the biomass-degrading fungus Trichoderma reesei (syn. Hypocrea jecorina). Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 553–560 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

