Ezrin Binds to DEAD-Box RNA Helicase DDX3 and Regulates Its Function and Protein Level
- PMID: 26149384
- PMCID: PMC4539380
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00332-15
Ezrin Binds to DEAD-Box RNA Helicase DDX3 and Regulates Its Function and Protein Level
Abstract
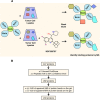
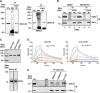
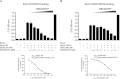
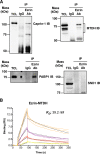
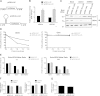
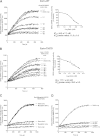
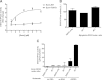
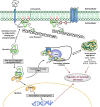
Ezrin is a key regulator of cancer metastasis that links the extracellular matrix to the actin cytoskeleton and regulates cell morphology and motility. We discovered a small-molecule inhibitor, NSC305787, that directly binds to ezrin and inhibits its function. In this study, we used a nano-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (nano-LC-MS-MS)-based proteomic approach to identify ezrin-interacting proteins that are competed away by NSC305787. A large number of the proteins that interact with ezrin were implicated in protein translation and stress granule dynamics. We validated direct interaction between ezrin and the RNA helicase DDX3, and NSC305787 blocked this interaction. Downregulation or long-term pharmacological inhibition of ezrin led to reduced DDX3 protein levels without changes in DDX3 mRNA. Ectopic overexpression of ezrin in low-ezrin-expressing osteosarcoma cells caused a notable increase in DDX3 protein levels. Ezrin inhibited the RNA helicase activity of DDX3 but increased its ATPase activity. Our data suggest that ezrin controls the translation of mRNAs preferentially with a structured 5' untranslated region, at least in part, by sustaining the protein level of DDX3 and/or regulating its function. Therefore, our findings suggest a novel function for ezrin in regulation of gene translation that is distinct from its canonical role as a cytoskeletal scaffold at the cell membrane.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Novel Ezrin Inhibitors Targeting Metastatic Osteosarcoma by Screening Open Access Malaria Box.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Nov;14(11):2497-507. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0511. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26358752 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin inhibit the invasive phenotype of osteosarcoma cells.Oncogene. 2012 Jan 19;31(3):269-81. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.245. Epub 2011 Jun 27. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 21706056 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ezrin in osteosarcoma metastasis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;804:181-201. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-04843-7_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24924175 Review.
-
Ezrin Inhibition Up-regulates Stress Response Gene Expression.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 17;291(25):13257-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.718189. Epub 2016 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27137931 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX3 in mRNA metabolism.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013 Jul-Aug;4(4):369-85. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1165. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013. PMID: 23606618 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Mechanotransduction in Osteosarcoma: A Comparative Oncology Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 14;21(20):7595. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207595. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33066583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the regulation of mRNA translation by scaffolding proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Dec 19;52(6):2569-2578. doi: 10.1042/BST20241021. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 39641595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of DEAD-Box RNA Helicase 3 attenuates stress granule assembly.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;182:114280. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114280. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33049245 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting RNA helicases in cancer: The translation trap.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017 Dec;1868(2):510-520. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28965870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ezrin accelerates breast cancer liver metastasis through promoting furin-like convertase-mediated cleavage of Notch1.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023 Jun;46(3):571-587. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00761-x. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023. PMID: 36580262
References
-
- Takeuchi K, Kawashima A, Nagafuchi A, Tsukita S. 1994. Structural diversity of band 4.1 superfamily members. J Cell Sci 107:1921–1928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
