Towards self-assembled hybrid artificial cells: novel bottom-up approaches to functional synthetic membranes
- PMID: 26149747
- PMCID: PMC4617832
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201501229
Towards self-assembled hybrid artificial cells: novel bottom-up approaches to functional synthetic membranes
Abstract
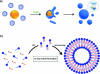
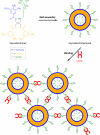
There has been increasing interest in utilizing bottom-up approaches to develop synthetic cells. A popular methodology is the integration of functionalized synthetic membranes with biological systems, producing "hybrid" artificial cells. This Concept article covers recent advances and the current state-of-the-art of such hybrid systems. Specifically, we describe minimal supramolecular constructs that faithfully mimic the structure and/or function of living cells, often by controlling the assembly of highly ordered membrane architectures with defined functionality. These studies give us a deeper understanding of the nature of living systems, bring new insights into the origin of cellular life, and provide novel synthetic chassis for advancing synthetic biology.
Keywords: artificial cell; drug delivery; polymersome; synthetic biology; vesicles.
© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

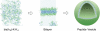


References
-
- Zhu TF, Adamala K, Zhang N, Szostak JW. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012;109:9828–9832. - PMC - PubMed
- Budin I, Debnath A, Szostak JW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:20812–20819. - PMC - PubMed
- Takakura K, Sugawara T. Langmuir. 2004;20:3832–3824. - PubMed
- Takakura K, Toyota T, Sugawara T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:8134–8140. - PubMed
-
- Blain JC, Szostak JW. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014;83:615–640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

