ALDH2(E487K) mutation increases protein turnover and promotes murine hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 26150517
- PMCID: PMC4517197
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1510757112
ALDH2(E487K) mutation increases protein turnover and promotes murine hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
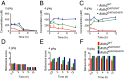
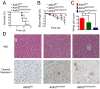
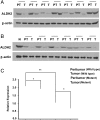
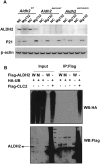
Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) in the liver removes toxic aldehydes including acetaldehyde, an intermediate of ethanol metabolism. Nearly 40% of East Asians inherit an inactive ALDH2*2 variant, which has a lysine-for-glutamate substitution at position 487 (E487K), and show a characteristic alcohol flush reaction after drinking and a higher risk for gastrointestinal cancers. Here we report the characterization of knockin mice in which the ALDH2(E487K) mutation is inserted into the endogenous murine Aldh2 locus. These mutants recapitulate essentially all human phenotypes including impaired clearance of acetaldehyde, increased sensitivity to acute or chronic alcohol-induced toxicity, and reduced ALDH2 expression due to a dominant-negative effect of the mutation. When treated with a chemical carcinogen, these mutants exhibit increased DNA damage response in hepatocytes, pronounced liver injury, and accelerated development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Importantly, ALDH2 protein levels are also significantly lower in patient HCC than in peritumor or normal liver tissues. Our results reveal that ALDH2 functions as a tumor suppressor by maintaining genomic stability in the liver, and the common human ALDH2 variant would present a significant risk factor for hepatocarcinogenesis. Our study suggests that the ALDH2*2 allele-alcohol interaction may be an even greater human public health hazard than previously appreciated.
Keywords: ALDH2*2 polymorphism; Asian flush; alcohol metabolism; liver cancer; mouse model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Yin SJ. Alcohol dehydrogenase: Enzymology and metabolism. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1994;2:113–119. - PubMed
-
- Matsuo K, et al. Gene-environment interaction between an aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 (ALDH2) polymorphism and alcohol consumption for the risk of esophageal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22(6):913–916. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi S, Matsushita S, Murayama M, Takagi S, Hayashida M. Alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase polymorphisms and the risk for alcoholism. Am J Psychiatry. 1995;152(8):1219–1221. - PubMed
-
- Baan R, et al. WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group Carcinogenicity of alcoholic beverages. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8(4):292–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

