A critical appraisal of ibrutinib in the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 26150724
- PMCID: PMC4484687
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S73559
A critical appraisal of ibrutinib in the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
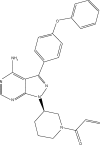
Although chemo-immunotherapy remains at the forefront of first-line treatment for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), small molecules, such as ibrutinib, are beginning to play a significant role, particularly in patients with multiply relapsed or chemotherapy-refractory disease and where toxicity is an overriding concern. Ibrutinib is a first-in-class, oral inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase, which functions by irreversible inhibition of the downstream signaling pathway of the B-cell receptor, which normally promotes cell survival and proliferation. Early clinical trials have demonstrated excellent tolerability and a modest side-effect profile even in elderly and multiply pretreated patient cohorts. Although the majority of disease responses tend to be partial, efficacy data have also been encouraging with more than two-thirds of patients with CLL and MCL demonstrating a durable response, even in the high-risk disease setting. Resistance mechanisms are only partially understood and appear to be multifactorial, including the binding site mutation C481S, and escape through other common cell-signaling pathways. This article appraises the currently available data on safety and efficacy from clinical trials of ibrutinib in the management of MCL and CLL, both as a single agent and in combination with other therapies, and considers how this drug is likely to be used in future clinical practice.
Keywords: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; chronic lymphocytic leukemia; ibrutinib; lymphoproliferative disorders; mantle cell lymphoma.
Figures
References
-
- Coiffier B, Haioun C, Ketterer N, et al. Rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) for the treatment of patients with relapsing or refractory aggressive lymphoma: a multicenter phase II study. Blood. 1998;92:1927–1932. - PubMed
-
- Delarue R, Haioun C, Ribrag V, et al. Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte (GELA) CHOP and DHAP plus rituximab followed by autologous stem cell transplantation in mantle cell lymphoma: a phase 2 study from the Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood. 2013;121(1):48–53. - PubMed
-
- Forstpointner R, Dreyling M, Repp R, et al. German Low-Grade Lymphoma Study Group The addition of rituximab to a combination of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, mitoxantrone (FCM) significantly increases the response rate and prolongs survival as compared with FCM alone in patients with relapsed and refractory follicular and mantle cell lymphomas: results of a prospective randomized study of the German Low-Grade Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 2015;104(10):3064–3072. - PubMed
-
- van Oers MH, Klasa R, Marcus RE, et al. Rituximab maintenance improves clinical outcome of relapsed/resistant follicular non-Hodgkin lymphoma in patients both with and without rituximab during induction: results of a prospective randomized phase 3 intergroup trial. Baseline. 2006;108(10):3295–3301. - PubMed
-
- Vose JM, Link BK, Grossbard ML, Czuczman M, Grillo-Lopez A, Fisher RI. Long-term update of a phase II study of rituximab in combination with CHOP chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated, aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46(11):1569–1573. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources