Physical and physiological effectiveness of an overall health care program for middle-aged Japanese women with mild obesity: A pilot study
- PMID: 26151017
- PMCID: PMC4488103
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2014.11.011
Physical and physiological effectiveness of an overall health care program for middle-aged Japanese women with mild obesity: A pilot study
Abstract
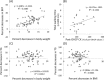
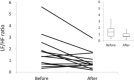
This study aimed to verify the effectiveness of an overall health care program (OHCP) for middle-aged Japanese women through assessing physical and physiological changes. The OHCP consisted of diet modification with natural alternative foods, walking and stretching exercises, and body massage and cupping treatments. Sixty-seven participants were assigned to one of three groups during a 3-year study period (2011-2013). The OHCP was performed for 3 months in each year. After the OHCP, most participants had significant decreases in the blood levels of triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, total cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase, γ-glutamyl transferase, and cholinesterase; body weight; body fat percentage; and body-mass index. The oxidative stress markers varied among the study years; however, a significant decrease in blood reactive oxygen-derived metabolites and a significant increase in the relative antioxidative potential were observed in 2013. In 2013, participants who were randomly selected for autonomic nervous activity measurements immediately before and after body massage and cupping treatments showed a significant predominance in parasympathetic nervous activity after the treatments. These results indicate that the OHCP in the present study is an effective and prompt method as a complementary treatment to improve the pre-obese or mild obese status without any noticeable physiological stress in most middle-aged women. However, because of the limitations of this study, the findings of this study need to be confirmed.
Keywords: autonomic nervous function; blood examination; body-mass index; middle-aged women; physiological stress.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Simple obesity in children. A study on the role of nutritional factors].Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006 Jan-Mar;10(1):3-191. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006. PMID: 16733288 Review. Polish.
-
The effect of weight management interventions that include a diet component on weight-related outcomes in pregnant and postpartum women: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):88-98. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1812. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447010
-
[The effectiveness of the treatment program "Enjoy eating" on health and mood in obese women].Laeknabladid. 2014 Jan;100(1):27-33. doi: 10.17992/lbl.2014.01.528. Laeknabladid. 2014. PMID: 24596968 Clinical Trial. Icelandic.
-
Serum concentration of adipocytokines in prepubertal vegetarian and omnivorous children.Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2011 Jul-Sep;15(3):326-34. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2011. PMID: 22006488
-
Offspring body size and metabolic profile - effects of lifestyle intervention in obese pregnant women.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4893. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123127 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Classical Massage on Biochemical Markers of Oxidative Stress in Humans: Pilot Study.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Dec 10;2021:6647250. doi: 10.1155/2021/6647250. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34926686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohan A., Lahiri A. Herbal medications and plastic surgery: a hidden danger. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;38:479–481. - PubMed
-
- Kamijo T., Murakami M. Regular physical exercise improves physical motor functions and biochemical markers in middle-age and elderly women. J Phys Act Health. 2009;6:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Hemmingsson E., Johansson K., Eriksson J., Sundström J., Neovius M., Marcus C. Weight loss and dropout during a commercial weight-loss program including a very-low-calorie diet, a low-calorie diet, or restricted normal food: observational cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;96:953–961. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morimoto A., Ohno Y., Tatsumi Y., Mizuno S., Watanabe S. Effects of healthy dietary pattern and other lifestyle factors on incidence of diabetes in a rural Japanese population. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2012;21:601–608. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
