Stemless shoulder arthroplasty: a literature review
- PMID: 26151038
- PMCID: PMC4469042
Stemless shoulder arthroplasty: a literature review
Abstract
The design of humeral implants for shoulder arthroplasty has evolved over the years. The new-generation modular shoulder prostheses have an anatomical humeral stem that replicates the three-dimensional parameters of the proximal humerus. An anatomical reconstruction is the best way to restore stability and mobility of the prosthetic shoulder and improve implant durability. However, a perfect anatomical match is not always possible in, for example, patients with post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the shoulder and deformities in the metaphyseal region. To avoid stem-related complications while retaining the advantages of the fourth generation of shoulder implants, different stemless implants have been developed. The stemless shoulder prosthesis is a new concept in shoulder arthroplasty. The authors review the indications, surgical technique, clinical and radiological midterm results, and complications of these humeral implants.
Keywords: arthroplasty; osteoarthritis; post-traumatic; shoulder; stemless.
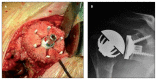
Figures

References
-
- Neer CS., 2nd Articular replacement for the humeral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1955;37-A:215–228. - PubMed
-
- Neer CS., 2nd Replacement arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Walch G, Boileau P. Prosthetic adaptability: a new concept for shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999;8:443–451. - PubMed
-
- Deshmukh AV, Koris M, Zurakowski D, Thornhill TS. Total shoulder arthroplasty: long-term survivorship, functional outcome, and quality of life. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14:471–479. - PubMed
-
- Sperling JW, Cofield RH, Rowland CM. Minimum fifteen-year follow-up of Neer hemiarthroplasty and total shoulder arthroplasty in patients aged fifty years or younger. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004;13:604–613. DOI: - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
