Anticancer Effect of Lycopene in Gastric Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 26151041
- PMCID: PMC4492364
- DOI: 10.15430/JCP.2015.20.2.92
Anticancer Effect of Lycopene in Gastric Carcinogenesis
Abstract
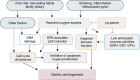
Gastric cancer ranks as the most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in the world. Risk factors of gastric carcinogenesis include oxidative stress, DNA damage, Helicobacter pylori infection, bad eating habits, and smoking. Since oxidative stress is related to DNA damage, smoking, and H. pylori infection, scavenging of reactive oxygen species may be beneficial for prevention of gastric carcinogenesis. Lycopene, one of the naturally occurring carotenoids, has unique structural and chemical features that contributes to a potent antioxidant activity. It shows a potential anticancer activity and reduces gastric cancer incidence. This review will summarize anticancer effect and mechanism of lycopene on gastric carcinogenesis based on the recent experimental and clinical studies.
Keywords: Anticancer effect; Gastric carcinogenesis; Lycopene.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lycopene inhibits Helicobacter pylori-induced ATM/ATR-dependent DNA damage response in gastric epithelial AGS cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Feb 1;52(3):607-615. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.11.010. Epub 2011 Nov 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22178412
-
Amelioration of oxidative stress with ensuing inflammation contributes to chemoprevention of H. pylori-associated gastric carcinogenesis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004 Jun;6(3):549-60. doi: 10.1089/152308604773934305. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004. PMID: 15130281 Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori-Mediated Genetic Instability and Gastric Carcinogenesis.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;400:305-323. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50520-6_13. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28124159 Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection, oxidative DNA damage, gastric carcinogenesis, and reversibility by rebamipide.Dig Dis Sci. 1998 Sep;43(9 Suppl):72S-77S. Dig Dis Sci. 1998. PMID: 9753230 Review.
-
A lucid review of Helicobacter pylori-induced DNA damage in gastric cancer.Helicobacter. 2019 Oct;24(5):e12631. doi: 10.1111/hel.12631. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Helicobacter. 2019. PMID: 31295756 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Trichoderma harzianum, 6-pentyl-α-pyrone and Plant Biopolymer Formulations Modulate Plant Metabolism and Fruit Quality of Plum Tomatoes.Plants (Basel). 2020 Jun 19;9(6):771. doi: 10.3390/plants9060771. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32575500 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic analysis reveals a transcriptional regulation network for the biosynthesis of carotenoids and flavonoids in 'Cara cara' navel Orange.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jan 7;21(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02808-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33413111 Free PMC article.
-
The andean anticancer herbal product BIRM causes destabilization of androgen receptor and induces caspase-8 mediated-apoptosis in prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):84201-84213. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12393. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27705939 Free PMC article.
-
The Anti-Cancer Activity of Lycopene: A Systematic Review of Human and Animal Studies.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 3;14(23):5152. doi: 10.3390/nu14235152. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36501182 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress: A Promising Target for Chemoprevention.Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2016 Apr;2(2):73-81. doi: 10.1007/s40495-016-0052-3. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27088073 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
