Identifying active vascular microcalcification by (18)F-sodium fluoride positron emission tomography
- PMID: 26151378
- PMCID: PMC4506997
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8495
Identifying active vascular microcalcification by (18)F-sodium fluoride positron emission tomography
Abstract
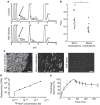
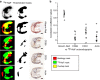
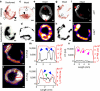
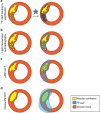
Vascular calcification is a complex biological process that is a hallmark of atherosclerosis. While macrocalcification confers plaque stability, microcalcification is a key feature of high-risk atheroma and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Positron emission tomography and X-ray computed tomography (PET/CT) imaging of atherosclerosis using (18)F-sodium fluoride ((18)F-NaF) has the potential to identify pathologically high-risk nascent microcalcification. However, the precise molecular mechanism of (18)F-NaF vascular uptake is still unknown. Here we use electron microscopy, autoradiography, histology and preclinical and clinical PET/CT to analyse (18)F-NaF binding. We show that (18)F-NaF adsorbs to calcified deposits within plaque with high affinity and is selective and specific. (18)F-NaF PET/CT imaging can distinguish between areas of macro- and microcalcification. This is the only currently available clinical imaging platform that can non-invasively detect microcalcification in active unstable atherosclerosis. The use of (18)F-NaF may foster new approaches to developing treatments for vascular calcification.
Figures

References
-
- Demer L. L. & Tintut Y. Mineral exploration: search for the mechanism of vascular calcification and beyond: the 2003 Jeffrey M. Hoeg Award lecture. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 1739–1743 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Johnson R. C., Leopold J. A. & Loscalzo J. Vascular calcification—Pathobiological mechanisms and clinical implications. Circ. Res. 99, 1044–1059 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Budoff M. J. et al.. Long-term prognosis associated with coronary calcification: observations from a registry of 25,253 patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 49, 1860–1870 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- A17242/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- PG/09/083/27667/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0701127/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 096823/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- FS/13/77/30488/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- WT103782AIA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 16465/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- FS/10/026/28209/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 16628/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- RG/13/14/30314/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/14/78/31020/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/12/29/29463/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- ETM/160/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- G0800784/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/12/8/29371/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 096823/Z/11/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 103782/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G1000847/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CH/09/002/26360/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- A16465/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- RG/10/007/28300/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 17242/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

