Low voltage alpha EEG phenotype is associated with reduced amplitudes of alpha event-related oscillations, increased cortical phase synchrony, and a low level of response to alcohol
- PMID: 26151497
- PMCID: PMC4579005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2015.07.002
Low voltage alpha EEG phenotype is associated with reduced amplitudes of alpha event-related oscillations, increased cortical phase synchrony, and a low level of response to alcohol
Abstract
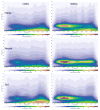
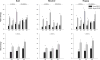
Low voltage EEG (LVEEG) is a heritable phenotype that differs depending on ancestral heritage, yet its impact on brain networks and cognition remain relatively unexplored. In this study we assessed energy and task related phase locking of event-related oscillation (EROs), behavioral responses, measures of IQ and personality, and expected responses to alcohol in a large sample of individuals with LVEEG compared to those with higher voltage variants. Participants (n=762) were recruited from a Native American community and completed a diagnostic interview, the Quick Test, the Subjective High Assessment Scale Expectation Version (SHAS-E) and the Maudsley Personality Inventory. Clinical and spectral analyzed EEGs were collected for determination of the presence of a LVEEG variant. EROs were generated using a facial expression recognition task. Participants with LVEEG (n=451) were significantly more likely to be older, married and have higher degrees of Native American heritage but did not differ in gender, income or education. Individuals with LVEEG were also found to have decreased energy in their alpha EROs, increased phase locking between stimulus trials, and increased phase-locking between cortical brain areas. No significant differences in the cognitive tests, personality variables or alcohol dependence or anxiety diagnoses were found, however, individuals with LVEEG did report a larger number of drinks ever consumed in a 24-h period and a less intense expected response to alcohol. These data suggest that alpha power in the resting EEG is highly associated with energy and cortical connectivity measures generated by event-related stimuli, as well as potentially increased risk for alcohol use.
Keywords: EEG phase synchrony; Event-related oscillations; Event-related potentials; Low voltage EEG.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures

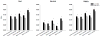
References
-
- Adrian ED, Matthews BHC. The Berger Rhythm: Potential changes from the occipital lobes in man. Brain. 1934;57:355–385. - PubMed
-
- Anokhin A, Steinlein O, Fischer C, Mao Y, Vogt P, Schalt E, Vogel F. A genetic study of the human low-voltage electroencephalogram. Hum Genet. 1992;90:99–112. - PubMed
-
- Arentsen K, Sindrup E. Electroencephalographic investigation of alcoholics. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1963;39:371–383. - PubMed
-
- Balconi M, Pozzoli U. Event-related oscillations (EROs) and event-related potentials (ERPs) comparison in facial expression recognition. J Neuropsychol. 2007;1:283–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

