Selective CNS Uptake of the GCP-II Inhibitor 2-PMPA following Intranasal Administration
- PMID: 26151906
- PMCID: PMC4494705
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131861
Selective CNS Uptake of the GCP-II Inhibitor 2-PMPA following Intranasal Administration
Abstract
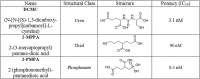
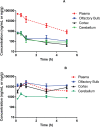
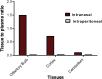
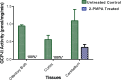
Glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCP-II) is a brain metallopeptidase that hydrolyzes the abundant neuropeptide N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate (NAAG) to NAA and glutamate. Small molecule GCP-II inhibitors increase brain NAAG, which activates mGluR3, decreases glutamate, and provide therapeutic utility in a variety of preclinical models of neurodegenerative diseases wherein excess glutamate is presumed pathogenic. Unfortunately no GCP-II inhibitor has advanced clinically, largely due to their highly polar nature resulting in insufficient oral bioavailability and limited brain penetration. Herein we report a non-invasive route for delivery of GCP-II inhibitors to the brain via intranasal (i.n.) administration. Three structurally distinct classes of GCP-II inhibitors were evaluated including DCMC (urea-based), 2-MPPA (thiol-based) and 2-PMPA (phosphonate-based). While all showed some brain penetration following i.n. administration, 2-PMPA exhibited the highest levels and was chosen for further evaluation. Compared to intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration, equivalent doses of i.n. administered 2-PMPA resulted in similar plasma exposures (AUC0-t, i.n./AUC0-t, i.p. = 1.0) but dramatically enhanced brain exposures in the olfactory bulb (AUC0-t, i.n./AUC0-t, i.p. = 67), cortex (AUC0-t, i.n./AUC0-t, i.p. = 46) and cerebellum (AUC0-t, i.n./AUC0-t, i.p. = 6.3). Following i.n. administration, the brain tissue to plasma ratio based on AUC0-t in the olfactory bulb, cortex, and cerebellum were 1.49, 0.71 and 0.10, respectively, compared to an i.p. brain tissue to plasma ratio of less than 0.02 in all areas. Furthermore, i.n. administration of 2-PMPA resulted in complete inhibition of brain GCP-II enzymatic activity ex-vivo confirming target engagement. Lastly, because the rodent nasal system is not similar to humans, we evaluated i.n. 2-PMPA also in a non-human primate. We report that i.n. 2-PMPA provides selective brain delivery with micromolar concentrations. These studies support intranasal delivery of 2-PMPA to deliver therapeutic concentrations in the brain and may facilitate its clinical development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioanalytical method for evaluating the pharmacokinetics of the GCP-II inhibitor 2-phosphonomethyl pentanedioic acid (2-PMPA).J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;88:162-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.08.028. Epub 2013 Aug 30. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 24055700 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Brain Delivery of 2-(Phosphonomethyl)pentanedioic Acid Following Intranasal Administration of Its γ-Substituted Ester Prodrugs.Mol Pharm. 2017 Oct 2;14(10):3248-3257. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00231. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Mol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28763226 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of NAAG peptidase inhibitor 2-PMPA in model chronic pain - relation to brain concentration.Neuropharmacology. 2006 Dec;51(7-8):1163-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.07.018. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Neuropharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16926034
-
Glutamate carboxypeptidase II (NAALADase) inhibition as a novel therapeutic strategy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;576:327-37; discussion 361-3. doi: 10.1007/0-387-30172-0_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 16802724 Review.
-
Progress in the discovery and development of glutamate carboxypeptidase II inhibitors.Drug Discov Today. 2007 Sep;12(17-18):767-76. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2007.07.010. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Drug Discov Today. 2007. PMID: 17826690 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphonates and Phosphonate Prodrugs in Medicinal Chemistry: Past Successes and Future Prospects.Front Chem. 2022 May 20;10:889737. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.889737. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35668826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII) inhibitor 2-PMPA reduces rewarding effects of the synthetic cathinone MDPV in rats: a role for N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG).Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Jun;234(11):1671-1681. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4568-y. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28251297 Free PMC article.
-
D-DOPA Is a Potent, Orally Bioavailable, Allosteric Inhibitor of Glutamate Carboxypeptidase II.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 23;14(10):2018. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102018. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297453 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of brain glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII) to enhance cognitive function.Adv Pharmacol. 2025;102:27-63. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2024.10.018. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Adv Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39929583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mathematical Modeling and Simulation to Investigate the CNS Transport Characteristics of Nanoemulsion-Based Drug Delivery Following Intranasal Administration.Pharm Res. 2019 Mar 28;36(5):75. doi: 10.1007/s11095-019-2610-y. Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 30923914
References
-
- Watkins JC. l-glutamate as a central neurotransmitter: looking back. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000; 28: 297–309. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter KJ, Dickenson AH. Amino acids are still as exciting as ever. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2001; 1: 57–61. - PubMed
-
- Slusher BS, Vornov JJ, Thomas AG, Hurn PD, Harukuni I, Bhardwaj A, et al. Selective inhibition of NAALADase, which converts NAAG to glutamate, reduces ischemic brain injury. Nat Med. 1999; 5: 1396–1402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

