Donor antigen-primed regulatory T cells permit liver regeneration and phenotype correction in hemophilia A mouse by allogeneic bone marrow stem cells
- PMID: 26152192
- PMCID: PMC4513683
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-015-0119-9
Donor antigen-primed regulatory T cells permit liver regeneration and phenotype correction in hemophilia A mouse by allogeneic bone marrow stem cells
Abstract
Introduction: Cell replacement therapy may be considered as an alternate approach to provide therapeutic dose of plasma factor VIII (FVIII) in patients with hemophilia A (HA). However, immune rejection limits the use of allogeneic cells in this mode of therapy. Here, we have examined the role of donor major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-stimulated host CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells in suppressing immune responses against allogeneic uncommitted (Lin(-)) bone marrow cells (BMCs) for correction of bleeding disorder in HA mice.
Methods: Allogeneic donor Lin(-) BMCs were co-transplanted with allo-antigen sensitized Treg cells in HA mice having acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury. Plasma FVIII activity was determined by in vitro functional assay, and correction of bleeding phenotype was assessed on the basis of capillary blood clotting time and tail-clip challenge. The immunosuppression potential of the sensitized Treg cells on CD4(+) T cells was studied both in vitro and in vivo. Suppression of inflammatory reactions in the liver against the homed donor cells by sensitized Treg cells was analysed by histopathological scoring. Allo-specificity of sensitized Treg cells and long-term retention of immunosuppression were examined against a third-party donor and by secondary challenge of allogeneic donor cells, respectively. The engraftment and phenotype change of donor BMCs in the liver and their role in synthesis of FVIII and liver regeneration were also determined.
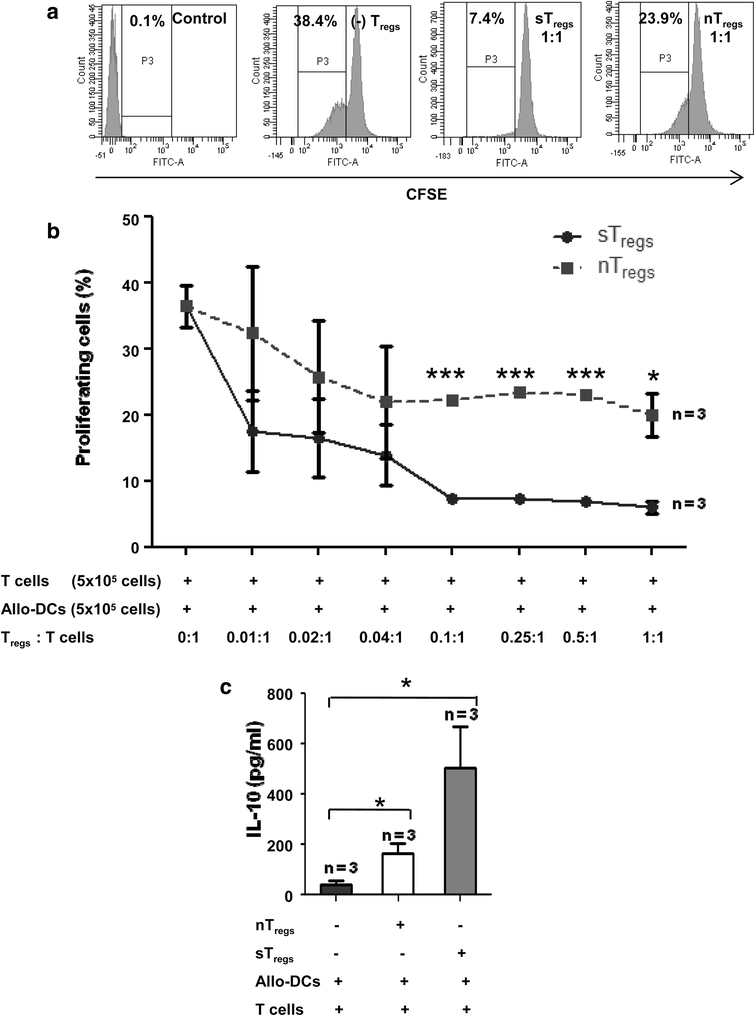
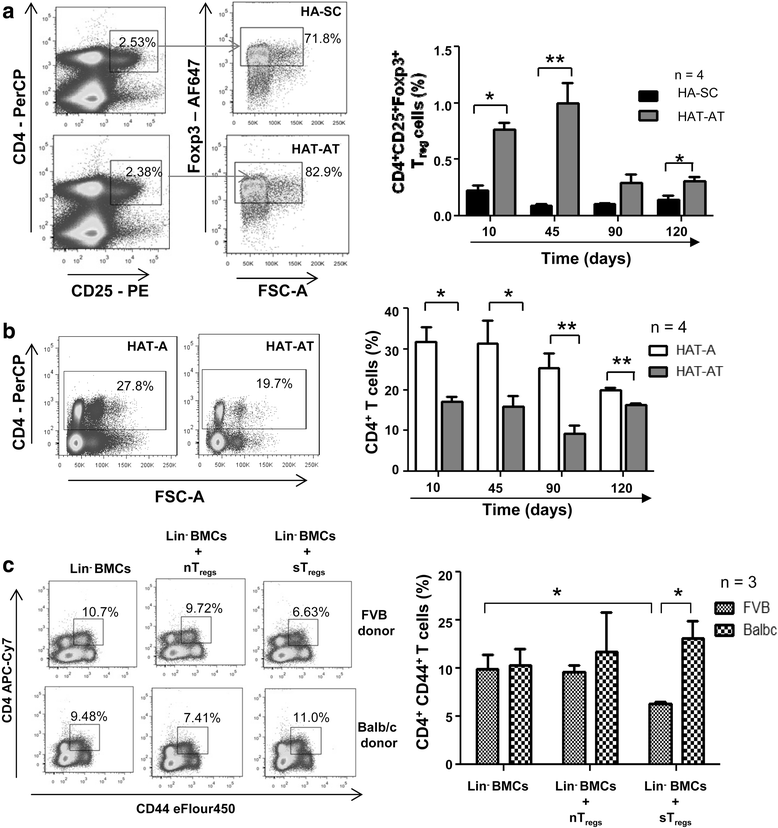
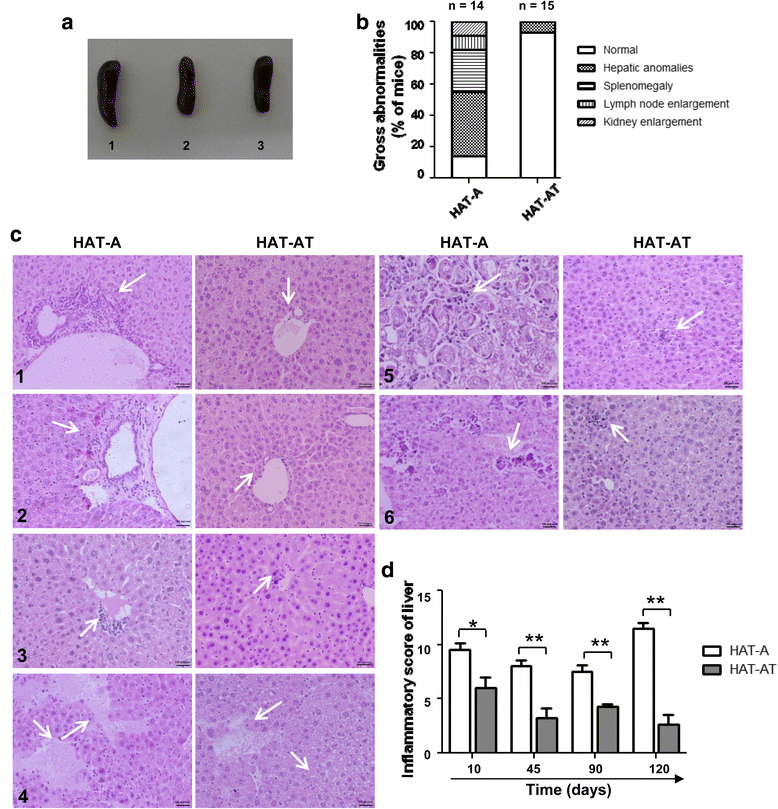
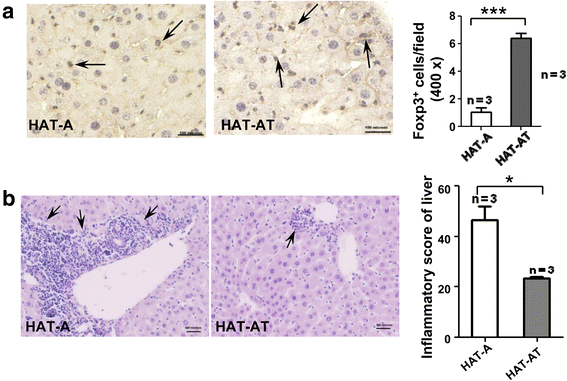
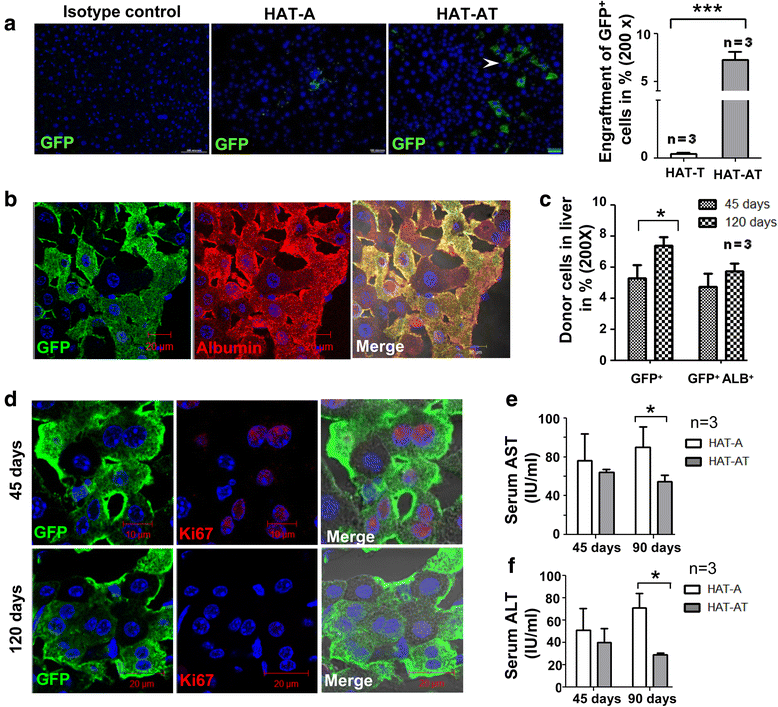
Results: Co-transplantation of allogeneic Lin(-) BMCs with sensitized Treg cells led to systemic immune modulation and suppression of inflammatory reactions in the liver, allowing better engraftment of allogeneic cells in the liver. Allo-antigen priming led to allo-specific immune suppression even after 1 year of transplantation. Donor-derived endothelial cells expressed FVIII in HA mice, leading to the correction of bleeding phenotype. Donor-derived hepatocyte-like cells, which constitute the major fraction of engrafted cells, supported regeneration of the liver after acute injury.
Conclusions: A highly proficient FVIII secreting core system can be created in regenerating liver by transplanting allogeneic Lin(-) BMCs in HA mice where transplantation tolerance against donor antigens can be induced by in vitro allo-antigen primed Treg cells. This strategy can be beneficial in treatment of genetic liver disorders for achieving prophylactic levels of the missing proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Factor VIII can be synthesized in hemophilia A mice liver by bone marrow progenitor cell-derived hepatocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Jan;21(1):110-20. doi: 10.1089/scd.2010.0569. Epub 2011 Jun 1. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 21480781
-
[Experimental study on rejection of allogeneic donor bone marrow cells in sensitized recipients].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Nov;32(11):734-8. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22339907 Chinese.
-
Donor bone marrow cells are essential for iNKT cell-mediated Foxp3+ Treg cell expansion in a murine model of transplantation tolerance.Eur J Immunol. 2017 Apr;47(4):734-742. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646670. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Eur J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28127757
-
Immunomodulation for inhibitors in hemophilia A: the important role of Treg cells.Expert Rev Hematol. 2010 Aug;3(4):469-83. doi: 10.1586/ehm.10.33. Expert Rev Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20976115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of regulatory T cells in tolerance to coagulation factors.J Thromb Haemost. 2009 Jul;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):88-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03417.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2009. PMID: 19630776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
JMJD3 aids in reprogramming of bone marrow progenitor cells to hepatic phenotype through epigenetic activation of hepatic transcription factors.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 22;12(3):e0173977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173977. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28328977 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin accessibility: biological functions, molecular mechanisms and therapeutic application.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Dec 4;9(1):340. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02030-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39627201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

