Rationale and Design of the Genomic Research in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and Sarcoidosis Study. Alpha-1 Protocol
- PMID: 26153726
- PMCID: PMC4627425
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201503-143OC
Rationale and Design of the Genomic Research in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and Sarcoidosis Study. Alpha-1 Protocol
Abstract
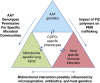
Severe deficiency of alpha-1 antitrypsin has a highly variable clinical presentation. The Genomic Research in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and Sarcoidosis α1 Study is a prospective, multicenter, cross-sectional study of adults older than age 35 years with PiZZ or PiMZ alpha-1 antitrypsin genotypes. It is designed to better understand if microbial factors influence this heterogeneity. Clinical symptoms, pulmonary function testing, computed chest tomography, exercise capacity, and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) will be used to define chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) phenotypes that can be studied with an integrated systems biology approach that includes plasma proteomics; mouth, BAL, and stool microbiome and virome analysis; and blood microRNA and blood mononuclear cell RNA and DNA profiling. We will rely on global genome, transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome datasets. Matched cohorts of PiZZ participants on or off alpha-1 antitrypsin augmentation therapy, PiMZ participants not on augmentation therapy, and control participants from the Subpopulations and Intermediate Outcome Measures in COPD Study who match on FEV1 and age will be compared. In the primary analysis, we will determine if the PiZZ individuals on augmentation therapy have a difference in lower respiratory tract microbes identified compared with matched PiZZ individuals who are not on augmentation therapy. By characterizing the microbiome in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), we hope to define new phenotypes of COPD that explain some of the diversity of clinical presentations. As a unique genetic cause of COPD, AATD may inform typical COPD pathogenesis, and better understanding of it may illuminate the complex interplay between environment and genetics. Although the biologic approaches are hypothesis generating, the results may lead to development of novel biomarkers, better understanding of COPD phenotypes, and development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic trials in AATD and COPD. Clinical trial registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT01832220).
Keywords: COPD; bronchoalveolar lavage; emphysema; lung; microbiome; phenotype.
Figures
References
-
- Stoller JK, Sandhaus RA, Turino G, Dickson R, Rodgers K, Strange C. Delay in diagnosis of α1-antitrypsin deficiency: a continuing problem. Chest. 2005;128:1989–1994. - PubMed
-
- McElvaney NG, Stoller JK, Buist AS, Prakash UB, Brantly ML, Schluchter MD, Crystal RD α1-Antitrypsin Deficiency Registry Study Group. Baseline characteristics of enrollees in the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Registry of α1-antitrypsin deficiency. Chest. 1997;111:394–403. - PubMed
-
- Eden E, Strange C, Holladay B, Xie L. Asthma and allergy in α-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Respir Med. 2006;100:1384–1391. - PubMed
-
- Needham M, Stockley RA. Exacerbations in α1-antitrypsin deficiency. Eur Respir J. 2005;25:992–1000. - PubMed
-
- Stockley RA, Bayley DL, Unsal I, Dowson LJ. The effect of augmentation therapy on bronchial inflammation in α1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1494–1498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 HL112694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL112711/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110883/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL114587/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL112702/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OH009077/OH/NIOSH CDC HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029882/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T15 LM007059/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL112696/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126600/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL112708/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL112707/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 OH009077/OH/NIOSH CDC HHS/United States
- 5 U24 OH009077/OH/NIOSH CDC HHS/United States
- U01 HL112695/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL112712/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 9 UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

