The Role of α-CTD in the Genome-Wide Transcriptional Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis Cells
- PMID: 26154296
- PMCID: PMC4495994
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131588
The Role of α-CTD in the Genome-Wide Transcriptional Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis Cells
Abstract
The amino acid sequence of the RNA polymerase (RNAP) α-subunit is well conserved throughout the Eubacteria. Its C-terminal domain (α-CTD) is important for the transcriptional regulation of specific promoters in both Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis, through interactions with transcription factors and/or a DNA element called the "UP element". However, there is only limited information regarding the α-CTD regulated genes in B. subtilis and the importance of this subunit in the transcriptional regulation of B. subtilis. Here, we established strains and the growth conditions in which the α-subunit of RNAP was replaced with a C-terminally truncated version. Transcriptomic and ChAP-chip analyses revealed that α-CTD deficiency reduced the transcription and RNAP binding of genes related to the utilization of secondary carbon sources, transition state responses, and ribosome synthesis. In E. coli, it is known that α-CTD also contributes to the expression of genes related to the utilization of secondary carbon sources and ribosome synthesis. Our results suggest that the biological importance of α-CTD is conserved in B. subtilis and E. coli, but that its specific roles have diversified between these two bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
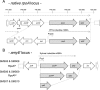

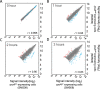


References
-
- Browning DF, Busby SJ (2004) The regulation of bacterial transcription initiation. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2: 57–65. - PubMed
-
- Moran CP Jr., Lang N, LeGrice SF, Lee G, Stephens M, Sonenshein AL, et al. (1982) Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis . Molecular & General Genetics 186: 339–346. - PubMed
-
- Dombroski AJ, Walter WA, Record MT Jr., Siegele DA, Gross CA (1992) Polypeptides containing highly conserved regions of transcription initiation factor sigma 70 exhibit specificity of binding to promoter DNA. Cell 70: 501–512. - PubMed
-
- Gourse RL, Ross W, Gaal T (2000) UPs and downs in bacterial transcription initiation: the role of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase in promoter recognition. Molecular Microbiology 37: 687–695. - PubMed
-
- Negishi T, Fujita N, Ishihama A (1995) Structural map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: structural domains identified by proteolytic cleavage. Journal of Molecular Biology 248: 723–728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

