Chromogranin A levels and mortality in patients with severe sepsis
- PMID: 26154393
- PMCID: PMC5027645
- DOI: 10.3109/1354750X.2015.1046932
Chromogranin A levels and mortality in patients with severe sepsis
Abstract
Context: Chromogranin A (CgA) is a novel biomarker with potential to assess mortality risk of patients with severe sepsis.
Objective: Assess association of CgA levels and mortality risk of severely septic patients.
Methods: Serum CgA levels were measured in 50 hospitalized, severely septic patients with organ failure <48 h.
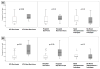
Results: Higher CgA levels trended toward higher ICU and hospital mortality. Patients without cardiovascular disease who died in the ICU had higher median (IQR) CgA levels 602.3 (343.3, 1134.3) ng/ml versus 205.5 (130.7, 325.9) ng/ml, p = 0.01.
Conclusions: High CgA levels predict ICU mortality in severely septic patients without prior cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Biological marker; Chromogranin A; cardiovascular diseases; mortality; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest
Figures

References
-
- Angelone T, Mazza R, Cerra MC. Chromogranin-A: a multifaceted cardiovascular role in health and disease. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19:4042–50. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, Wax RS. Epidemiology of sepsis: an update. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:S109–16. - PubMed
-
- Annane D, Aegerter P, Jars-Guincestre MC, Guidet B Network CU-R. Current epidemiology of septic shock: the CUB-Rea Network. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168:165–72. - PubMed
-
- Arora S, Singh P, Singh PM, Trikha A. Procalcitonin levels in survivors and non survivors of Sepsis: Systematic review and Meta-analysis. Shock 2014 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
