Immediate impact of rapid maxillary expansion on upper airway dimensions and on the quality of life of mouth breathers
- PMID: 26154455
- PMCID: PMC4520137
- DOI: 10.1590/2176-9451.20.3.043-049.oar
Immediate impact of rapid maxillary expansion on upper airway dimensions and on the quality of life of mouth breathers
Abstract
Objective: To assess short-term tomographic changes in the upper airway dimensions and quality of life of mouth breathers after rapid maxillary expansion (RME).
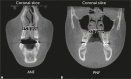
Methods: A total of 25 mouth breathers with maxillary atresia and a mean age of 10.5 years old were assessed by means of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and a standardized quality of life questionnaire answered by patients' parents/legal guardians before and immediately after rapid maxillary expansion.
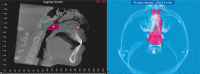
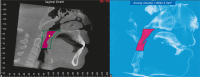
Results: Rapid maxillary expansion resulted in similar and significant expansion in the width of anterior (2.8 mm, p < 0.001) and posterior nasal floor (2.8 mm, p < 0.001). Although nasopharynx and nasal cavities airway volumes significantly increased (+1646.1 mm3, p < 0.001), oropharynx volume increase was not statistically significant (+1450.6 mm3, p = 0.066). The results of the quality of life questionnaire indicated that soon after rapid maxillary expansion, patients' respiratory symptoms significantly decreased in relation to their initial respiratory conditions.
Conclusions: It is suggested that RME produces significant dimensional increase in the nasal cavity and nasopharynx. Additionally, it also positively impacts the quality of life of mouth-breathing patients with maxillary atresia.
OBJETIVO:: avaliar, por meio de tomografias, as mudanças em curto prazo nas vias aéreas superiores e na qualidade de vida em pacientes respiradores bucais, após expansão rápida da maxila (ERM).
MÉTODOS:: foram avaliados 25 pacientes respiradores bucais com atresia maxilar, com idade média de 10,5 anos, por meio de tomografia computadorizada de feixe cônico (TCFC) e questionário padronizado de qualidade de vida submetido aos pais/responsáveis, antes e imediatamente após a ERM.
RESULTADOS:: a ERM promoveu uma expansão, de forma semelhante e significativa, tanto na largura do soalho nasal anterior (2,8mm, p < 0,001) quanto na largura do soalho nasal posterior (2,8mm, p < 0,001). No volume aéreo da nasofaringe e fossas nasais, houve aumento significativo (+1646,1mm p < 0,001); entretanto, no volume aéreo da orofaringe, houve aumento não significativo (+1450,6 mm p = 0,066). Os resultados do questionário de qualidade de vida indicaram melhora significativa na qualidade de vida dos pacientes após a ERM, em comparação ao questionário inicial.
CONCLUSÕES:: a ERM promoveu aumento dimensional significativo nas fossas nasais e na nasofaringe, bem como melhorou significativamente a qualidade de vida dos pacientes.
Figures
References
-
- McNamara JA., Jr A method of cephalometric evaluation. Am J Orthod. 1984;86(6):449–469. - PubMed
-
- Oulis CJ, Vadiaskas GP, Ekonomides J, Dratsa J. The effect of hypertrophic adenoids and tonsils on the development of posterior crossbite and oral habits. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 1994;18(3):197–201. - PubMed
-
- Thilander B, Wahlund S, Lennartsson B. The effect of early interceptive treatment in children with posterior cross-bite. Eur J Orthod. 1984;6(1):25–34. - PubMed
-
- Viazis AD. Efficient orthodontic treatment timing. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1995;108(5):560–561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

