Urinary uromodulin, kidney function, and cardiovascular disease in elderly adults
- PMID: 26154925
- PMCID: PMC4653069
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2015.192
Urinary uromodulin, kidney function, and cardiovascular disease in elderly adults
Abstract
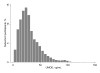
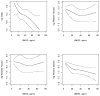
Urinary uromodulin (uUMOD) is the most common secreted tubular protein in healthy adults. However, the relationship between uUMOD and clinical outcomes is still unclear. Here we measured uUMOD in 192 participants of the Cardiovascular Health Study with over a 30% decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) over 9 years, 54 with incident end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and in a random subcohort of 958 participants. The association of uUMOD with eGFR decline was evaluated using logistic regression and with incident ESRD, cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and mortality using Cox proportional regression. Mean age was 78 years and median uUMOD was 25.8 μg/ml. In a case-control study evaluating eGFR decline (192 cases and 231 controls), each 1-s.d. higher uUMOD was associated with a 23% lower odds of eGFR decline (odds ratio 0.77 (95% CI 0.62-0.96)) and a 10% lower risk of mortality (hazard ratio 0.90 (95% CI 0.83-0.98)) after adjusting for demographics, eGFR, albumin/creatinine ratio, and other risk factors. There was no risk association of uUMOD with ESRD, cardiovascular disease, or heart failure after multivariable adjustment. Thus, low uUMOD levels may identify persons at risk of progressive kidney disease and mortality above and beyond established markers of kidney disease, namely eGFR and the albumin/creatinine ratio. Future studies need to confirm these results and evaluate whether uUMOD is a marker of tubular health and/or whether it plays a causal role in preserving kidney function.
Figures
Comment in
-
Uromodulin, kidney function, cardiovascular disease, and mortality.Kidney Int. 2015 Nov;88(5):944-6. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.267. Kidney Int. 2015. PMID: 26579681
References
-
- Stevens LA, Li S, Wang C, et al. Prevalence of CKD and comorbid illness in elderly patients in the United States: results from the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) American journal of kidney diseases : the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation. 2010;55(3 Suppl 2):S23–33. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Briet M, Bozec E, Laurent S, et al. Arterial stiffness and enlargement in mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2006;69(2):350–7. - PubMed
-
- Vlagopoulos PT, Tighiouart H, Weiner DE, et al. Anemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in diabetes: the impact of chronic kidney disease. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN. 2005;16(11):3403–10. - PubMed
-
- Lhotta K. Uromodulin and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2010;33(5):393–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01HC-85081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098234/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-85085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-85084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-85080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-85083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC85239/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007777/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG027002/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-54133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-35129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DK096418/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027002/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-15103/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 DK007777-13/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC-85082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

