Relationship between hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia and renal severity in patients with lupus nephritis: a prospective study
- PMID: 26155131
- PMCID: PMC4440014
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2014.43730
Relationship between hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia and renal severity in patients with lupus nephritis: a prospective study
Abstract
Aim of the study: The purpose is to evaluate the relationship between hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, nephrotic and renal severity in patients with lupus nephritis.
Material and methods: Autoantibodies and serological parameters were measured and analyzed in 429 patients with lupus nephritis in a single centre.
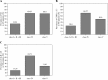
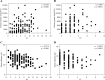
Results: The prevalence for anti-dsDNA, anti-nucleosome and anti-histone was higher in the nephrotic syndrome (NS) patients than that in non-NS patients (p < 0.0001 for all comparisons). The NS patients had a higher proportion of diffuse proliferative renal lesions (69.05%) and membranous lesions (68.00%). Serum total cholesterol and albumin levels were associated with activity and severity of renal disease. The levels of proteinuria and serum albumin were positively correlated with activity and chronicity index (p < 0.001 for all correlations). The incidence of a poor renal outcome (p = 0.0461) in the NS patients was significantly increased. On the other hand, the remission rate (p = 0.0002) was significantly reduced and recurrence rate (p = 0.0027) was significantly increased in NS patients.
Conclusions: This paper highlights that nephrotic-range proteinuria, elevated total cholesterol level and decreased serum albumin levels may reflect the activity and severity of renal damage in SLE patients.
Keywords: activity; hyperlipidemia; hypoalbuminemia; renal damage; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The value of early renal biopsy in systemic lupus erythematosus patients presenting with renal involvement.Clin Nephrol. 2012 Jan;77(1):18-24. doi: 10.5414/cn107094. Clin Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22185964
-
Measurement of autoantibodies in pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematosus and their relationship with disease-associated manifestations.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Jun;41(6):840-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2011.09.009. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22177108
-
Lupus nephritis: the significance of serological tests at the time of biopsy.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1991 Jul-Aug;9(4):345-9. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1991. PMID: 1934681
-
Anti-dsDNA, anti-nucleosome and anti-C1q antibodies as disease activity markers in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2014 Jul-Aug;142(7-8):431-6. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2014. PMID: 25233687
-
Morphological Indexes: Can They Predict Lupus Nephritis Outcomes? A Retrospective Study.Acta Med Port. 2019 Oct 1;32(10):635-640. doi: 10.20344/amp.11598. Acta Med Port. 2019. PMID: 31625875
Cited by
-
Urinary Albumin Levels are Independently Associated with Renal Lesion Severity in Patients with Lupus Nephritis and Little or No Proteinuria.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Feb 3;23:631-639. doi: 10.12659/msm.899973. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28157833 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of remnant cholesterol on adverse renal outcomes in lupus nephritis.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Apr 10;24(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02503-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40211319 Free PMC article.
-
Serum albumin and beta-amyloid deposition in the human brain.Neurology. 2020 Aug 18;95(7):e815-e826. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010005. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 32690787 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of the Total Cholesterol/high-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio with Outcomes in Lupus Nephritis.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Apr 28;22(10):2398-2407. doi: 10.7150/ijms.106393. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40386044 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic Nutritional Index and Nutritional Risk Index Are Associated with Disease Activity in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Nutrients. 2019 Mar 16;11(3):638. doi: 10.3390/nu11030638. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30884776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jakes RW, Bae SC, Louthrenoo W, et al. Systematic review of the epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus in the Asia-Pacific region: prevalence, incidence, clinical features, and mortality. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2012;64:159–168. - PubMed
-
- Osio-Salido E, Manapat-Reyes H. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus in Asia. Lupus. 2010;19:1365–1373. - PubMed
-
- Burlingame RW, Cervera R. Anti-chromatin (anti-nucleosome) autoantibodies. Autoimmun Rev. 2002;1:321–328. - PubMed
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Oka Y, Tada M, et al. A potential trigger of nephritogenic anti-DNA antibodies in lupus nephritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1108:92–95. - PubMed
-
- Mortensen ES, Rekvig OP. Nephritogenic potential of anti-DNA antibodies against necrotic nucleosomes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:696–704. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
