Possible role of complement factors and their inhibitors in the myocardial infarction: an immunohistochemical study
- PMID: 26155132
- PMCID: PMC4440022
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2014.43731
Possible role of complement factors and their inhibitors in the myocardial infarction: an immunohistochemical study
Abstract
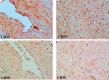
Ongoing development of our civilization is accompanied by a marked increase of incidence of cardiovascular diseases and cardiovascular mortality. Ischemic heart disease with its extreme form - myocardial infarction - is one of the main problems of modern medicine. Despite much research devoted to this disease entity, its pathomechanism remains incompletely understood. Basing on research reports, more and more emphasis is put on immune reactions in the myocardium. Available literature lacks detailed studies examining the role of complement system and its inhibitors in the development and pathogenesis of myocardial infarction. Cells of ischemic myocardium were proven to become foreign antigens for the immune system of the patient's body. This results in complement activation of formation of so called membrane attacking complex that injures myocardial cells. By binding to its surface, it extends the myocardial destruction caused by the infarction itself. Results of immunochemistry studies presented in this paper have demonstrated the existence colocalization of complement components (C4d, C9) and membrane inhibitors (CD55, CD59) as well as soluble inhibitors (factor H) of the complement in the examined muscle tissue that underwent ischemic necrosis. Positive immunohistochemical reaction was found in the myocardial cells, intercellular matrix and blood vessels.
Keywords: complement inhibitors; complement system; myocardial infarction.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Time course of complement activation and inhibitor expression after ischemic injury of rat myocardium.Am J Pathol. 1994 Jun;144(6):1357-68. Am J Pathol. 1994. PMID: 7515561 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of expression of protectin (CD59) is associated with complement membrane attack complex deposition in myocardial infarction.Lab Invest. 1992 Nov;67(5):608-16. Lab Invest. 1992. PMID: 1279272
-
The study of the protein complement in myocardial infarction.Immunol Lett. 2014 Nov;162(1 Pt A):262-8. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2014.09.015. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Immunol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25256773
-
Prevention of ventricular fibrillation, acute myocardial infarction (myocardial necrosis), heart failure, and mortality by bretylium: is ischemic heart disease primarily adrenergic cardiovascular disease?Am J Ther. 2004 Sep-Oct;11(5):366-411. doi: 10.1097/01.mjt.0000126444.24163.81. Am J Ther. 2004. PMID: 15356432 Review.
-
The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Res. 2002 Jan;53(1):31-47. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(01)00434-5. Cardiovasc Res. 2002. PMID: 11744011 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular tissue changes in early myocardial ischemia: from pathophysiology to the identification of new diagnostic markers.Int J Legal Med. 2018 Mar;132(2):425-438. doi: 10.1007/s00414-017-1750-z. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Int J Legal Med. 2018. PMID: 29362873 Review.
References
-
- Derzhko R, Witkowska M. Glucose metabolism disturbances and the risk of cardiovascular diseases (in Polish) Adr Clin Exp Med. 2010;5:911–916.
-
- De Backer G, Ambrosioni E, Borch-Johnsen K, et al. Third Joint Task Force of European and other Societies on Cardiovascular Diseases Prevention in Clinical Practice. European guidelines on cardiovascular diseases prevention in clinical practice. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:1601–1610. - PubMed
-
- Podolec P, Kopeć G, Pająk A. Konsensus Rady Redakcyjnej Polskiego Forum Profilaktyki Chorób Układu Krążenia dotyczący oceny ryzyka sercowo-naczyniowego. Forum Profilaktyki. 2006;2:2. - PubMed
-
- Alpert JS, Thygesen K, Antman E, Bassand JP. Myocardial infarction redefined – a consensus document of the Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology/Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 21: 1502-1513. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:959–969. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
