CD4+CD25(high), CD8+CD28- cells and thyroid autoantibodies in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 26155145
- PMCID: PMC4439998
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2014.45945
CD4+CD25(high), CD8+CD28- cells and thyroid autoantibodies in breast cancer patients
Abstract
Aim of the study: To investigate the percentage of CD4+CD25(high) cells (including Treg cells) and CD8+CD28- cells in breast cancer patients with and without high levels of autoimmune thyroid antibodies.
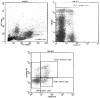
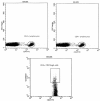
Material and methods: Thirty-five women with breast cancer (9 of them having high thyroid antibodies) and fourteen healthy subjects were enrolled in this study. Flow cytometry was used to count CD4+CD25(high) cells and CD8+CD28- suppressive cells (CD8 cell subtypes).
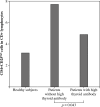
Results: In the patient group, the percentage of CD28- cells in CD8+ lymphocytes were higher [67.50% (55.1180.33) vs. 51.56% (42.5766.38); p = 0.021] and the percentage of CD28+CD45RO- cells (memory cells) in CD8+ lymphocytes were lower than in the control group. CD4+CD25(high) cell percentage in CD4+ lymphocytes was elevated in the patient group [6.44% (4.528.74) vs. 2.97% (1.724.34); p < 0.001]. When the cytometric parameters were compared between patients (with high vs. normal thyroid antibodies), the distribution of CD8+ cell subgroups was also similar. CD4+CD25(high) cells among CD4+ lymphocytes were decreased in patients with high levels of thyroid antibodies [5.19% (3.426.17) vs. 6.99% (4.829.95); p = 0.043].
Conclusions: CD4+CD25(high) cells may play a role in autoimmunity of breast cancer patients, and may be a predictive marker. Advanced studies which evaluate the possible links between regulatory cells and autoimmunity should be established in cancer patients.
Keywords: Treg cells; autoimmunity; breast cancer; thyroid antibody.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ and CD8+CD28- regulatory T cells in non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing surgery.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Feb;18(2):255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24345703
-
[The change of periphery and centra CD4(+);CD25(+);Treg, CD8(+);CD28(-);Treg in the MOG induced model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Aug;26(8):746-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20619099 Chinese.
-
Distribution and clinical significance of circulating CD8+CD28- regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Jul 30;22(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02088-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35907816 Free PMC article.
-
[Changes of CD4+ CD25+ and CD8+ CD28- T regulatory cells in spontaneous tolerance of inbred rat orthotopic liver transplantation].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006 Jun 18;38(3):266-70. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006. PMID: 16778969 Chinese.
-
Breast cancer in previously thyroidectomized patients: which thyroid disorders are a risk factor?Future Sci OA. 2021 Mar 29;7(5):FSO699. doi: 10.2144/fsoa-2021-0029. Future Sci OA. 2021. PMID: 34046196 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grani G, Dicorato P, Dainelli M, et al. Thyroid diseases in women with breast cancer. Clin Ter. 2012;163:e401–e404. - PubMed
-
- Hardefeldt PJ, Eslick GD, Edirimanne S. Benign thyroid disease is associated with breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;133:1169–1177. - PubMed
-
- Morris GP, Kong YC. Tolerance to autoimmune thyroiditis: (CD4+)CD25+ regulatory T cells influence susceptibility but do not supersede MHC class II restriction. Front Biosci. 2006;11:1234–1243. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
