Psychosocial treatment and interventions for bipolar disorder: a systematic review
- PMID: 26155299
- PMCID: PMC4493813
- DOI: 10.1186/s12991-015-0057-z
Psychosocial treatment and interventions for bipolar disorder: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Bipolar disorder (BD) is a chronic disorder with a high relapse rate, significant general disability and burden and with a psychosocial impairment that often persists despite pharmacotherapy. This indicates the need for effective and affordable adjunctive psychosocial interventions, tailored to the individual patient. Several psychotherapeutic techniques have tried to fill this gap, but which intervention is suitable for each patient remains unknown and it depends on the phase of the illness.
Methods: The papers were located with searches in PubMed/MEDLINE through May 1st 2015 with a combination of key words. The review followed the recommendations of the Preferred Items for Reporting of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement.
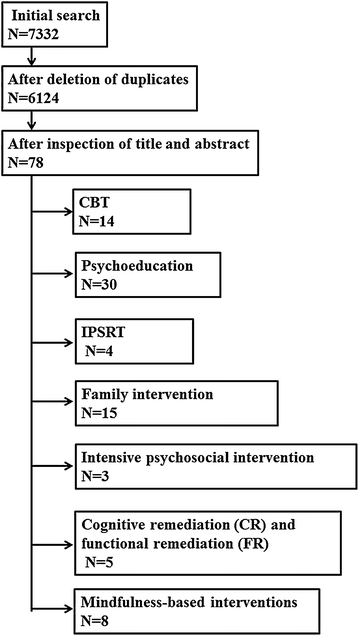
Results: The search returned 7,332 papers; after the deletion of duplicates, 6,124 remained and eventually 78 were included for the analysis. The literature supports the usefulness only of psychoeducation for the relapse prevention of mood episodes and only in a selected subgroup of patients at an early stage of the disease who have very good, if not complete remission, of the acute episode. Cognitive-behavioural therapy and interpersonal and social rhythms therapy could have some beneficial effect during the acute phase, but more data are needed. Mindfulness interventions could only decrease anxiety, while interventions to improve neurocognition seem to be rather ineffective. Family intervention seems to have benefits mainly for caregivers, but it is uncertain whether they have an effect on patient outcomes.
Conclusion: The current review suggests that the literature supports the usefulness only of specific psychosocial interventions targeting specific aspects of BD in selected subgroups of patients.
Similar articles
-
The neurocognitive functioning in bipolar disorder: a systematic review of data.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2015 Dec 1;14:42. doi: 10.1186/s12991-015-0081-z. eCollection 2015. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26628905 Free PMC article.
-
Psychosocial interventions in bipolar disorder: what, for whom, and when.J Affect Disord. 2014 Mar;156:46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.12.017. Epub 2013 Dec 25. J Affect Disord. 2014. PMID: 24439829 Review.
-
Psychotherapeutic intervention and suicide risk reduction in bipolar disorder: a review of the evidence.J Affect Disord. 2009 Feb;113(1-2):21-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2008.06.014. Epub 2008 Aug 3. J Affect Disord. 2009. PMID: 18676024 Review.
-
The package of care for patients with bipolar depression.J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66 Suppl 5:34-9. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16038600 Review.
-
Empirically supported psychosocial interventions for bipolar disorder: Current state of the research.J Affect Disord. 2016 Sep 1;201:203-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.05.018. Epub 2016 May 14. J Affect Disord. 2016. PMID: 27243619 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence-Based Psychotherapies for Bipolar Disorder.Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2019 Jul;17(3):238-248. doi: 10.1176/appi.focus.20190004. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2019. PMID: 32047369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative approaches to bipolar disorder and its treatment.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016 Feb;1366(1):76-89. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13048. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016. PMID: 27111134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations between family cohesion, adaptability, and functioning of patients with bipolar disorder with clinical syndromes in Hebei, China.J Int Med Res. 2019 Dec;47(12):6004-6015. doi: 10.1177/0300060519877030. Epub 2019 Oct 20. J Int Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31631724 Free PMC article.
-
Mindfulness meditation for workplace wellness: An evidence map.Work. 2019;63(2):205-218. doi: 10.3233/WOR-192922. Work. 2019. PMID: 31156202 Free PMC article.
-
Domain-Specific Memory Impairments in Bipolar Mania: Insights from a Tertiary Care Hospital.Indian J Psychol Med. 2025 Jan 30:02537176241312646. doi: 10.1177/02537176241312646. Online ahead of print. Indian J Psychol Med. 2025. PMID: 39897717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fountoulakis KN, Kasper S, Andreassen O, Blier P, Okasha A, Severus E, et al. Efficacy of pharmacotherapy in bipolar disorder: a report by the WPA section on pharmacopsychiatry. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2012;262(Suppl 1):1–48. - PubMed
-
- Grunze H, Vieta E, Goodwin GM, Bowden C, Licht RW, Moller HJ, et al. The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for the biological treatment of bipolar disorders: update 2012 on the long-term treatment of bipolar disorder. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2013;14(3):154–219. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2197–2223. - PubMed
-
- Rosa AR, Reinares M, Michalak EE, Bonnin CM, Sole B, Franco C, et al. Functional impairment and disability across mood states in bipolar disorder. Value Health. 2010;13(8):984–988. - PubMed
-
- Tohen M, Hennen J, Zarate CM, Jr, Baldessarini RJ, Strakowski SM, Stoll AL, et al. Two-year syndromal and functional recovery in 219 cases of first-episode major affective disorder with psychotic features. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157(2):220–228. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous