Olive oil consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes in US women
- PMID: 26156740
- PMCID: PMC4515873
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.115.112029
Olive oil consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes in US women
Abstract
Background: Olive oil has been shown to improve various cardiometabolic risk factors. However, to our knowledge, the association between olive oil intake and type 2 diabetes (T2D) has never been evaluated in the US population.
Objective: We aimed to examine the association between olive oil intake and incident T2D.
Design: We followed 59,930 women aged 37-65 y from the Nurses' Health Study (NHS) and 85,157 women aged 26-45 y from the NHS II who were free of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer at baseline. Diet was assessed by validated food-frequency questionnaires, and data were updated every 4 y. Incident cases of T2D were identified through self-report and confirmed by supplementary questionnaires.
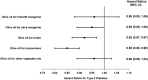
Results: After 22 y of follow-up, we documented 5738 and 3914 incident cases of T2D in the NHS and NHS II, respectively. With the use of Cox regression models with repeated measurements of diet and multivariate adjustment for major lifestyle and dietary factors, the pooled HR (95% CI) of T2D in those who consumed >1 tablespoon (>8 g) of total olive oil per day compared with those who never consumed olive oil was 0.90 (0.82, 0.99). The corresponding HRs (95% CIs) were 0.95 (0.87, 1.04) for salad dressing olive oil and 0.85 (0.74, 0.98) for olive oil added to food or bread. We estimated that substituting olive oil (8 g/d) for stick margarine, butter, or mayonnaise was associated with 5%, 8%, and 15% lower risk of T2D, respectively, in the pooled analysis of both cohorts.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that higher olive oil intake is associated with modestly lower risk of T2D in women and that hypothetically substituting other types of fats and salad dressings (stick margarine, butter, and mayonnaise) with olive oil is inversely associated with T2D.
Keywords: Nurses’ Health Study; diet; dietary fat; olive oil; salad dressing; type 2 diabetes.
© 2015 American Society for Nutrition.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas, 6th ed. Brussels (Belgium): International Diabetes Federation, 2013.
-
- Narayan KM, Gregg EW, Fagot-Campagna A, Engelgau MM, Vinicor F. Diabetes—a common, growing, serious, costly, and potentially preventable public health problem. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2000;50(Suppl 2):S77–84. - PubMed
-
- Hu FB, van Dam RM, Liu S. Diet and risk of type II diabetes: the role of types of fat and carbohydrate. Diabetologia 2001;44:805–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

