Elimination of Microglia Improves Functional Outcomes Following Extensive Neuronal Loss in the Hippocampus
- PMID: 26156998
- PMCID: PMC4495246
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0336-15.2015
Elimination of Microglia Improves Functional Outcomes Following Extensive Neuronal Loss in the Hippocampus
Abstract
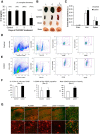
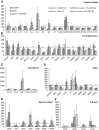
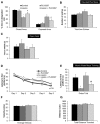
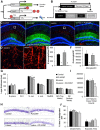
With severe injury or disease, microglia become chronically activated and damage the local brain environment, likely contributing to cognitive decline. We previously discovered that microglia are dependent on colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) signaling for survival in the healthy adult brain, and we have exploited this dependence to determine whether such activated microglia contribute deleteriously to functional recovery following a neuronal lesion. Here, we induced a hippocampal lesion in mice for 25 d via neuronal expression of diphtheria toxin A-chain, producing both a neuroinflammatory reaction and behavioral alterations. Following the 25 d lesion, we administered PLX3397, a CSF1R inhibitor, for 30 d to eliminate microglia. This post-lesion treatment paradigm improved functional recovery on elevated plus maze and Morris water maze, concomitant with reductions in elevated proinflammatory molecules, as well as normalization of lesion-induced alterations in synaptophysin and PSD-95. Further exploration of the effects of microglia on synapses in a second cohort of mice revealed that dendritic spine densities are increased with long-term microglial elimination, providing evidence that microglia shape the synaptic landscape in the adult mouse brain. Furthermore, in these same animals, we determined that microglia play a protective role during lesioning, whereby neuronal loss was potentiated in the absence of these cells. Collectively, we demonstrate that microglia exert beneficial effects during a diphtheria toxin-induced neuronal lesion, but impede recovery following insult.
Significance statement: It remains unknown to what degree, and by what mechanisms, chronically activated microglia contribute to cognitive deficits associated with brain insults. We induced a genetic neuronal lesion in mice for 25 d and found activated microglia to increase inflammation, alter synaptic surrogates, and impede behavioral recovery. These lesion-associated deficits were ameliorated with subsequent microglial elimination, underscoring the importance of developing therapeutics aimed at eliminating/modulating chronic microglial activation. Additionally, we found long-term microglial depletion globally increases dendritic spines by ∼35% in the adult brain, indicating that microglia continue to sculpt the synaptic landscape in the postdevelopmental brain under homeostatic conditions. Microglial manipulation can therefore be used to investigate the utility of increasing dendritic spine numbers in postnatal conditions displaying synaptic aberrations.
Keywords: behavior; glia; inflammation; lesion; spines; synapse.
Copyright © 2015 the authors 0270-6474/15/359977-13$15.00/0.
Figures



References
-
- Beschorner R, Nguyen TD, Gözalan F, Pedal I, Mattern R, Schluesener HJ, Meyermann R, Schwab JM. CD14 expression by activated parenchymal microglia/macrophages and infiltrating monocytes following human traumatic brain injury. Acta Neuropathologica. 2002;103:541–549. doi: 10.1007/s00401-001-0503-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Butovsky O, Siddiqui S, Gabriely G, Lanser AJ, Dake B, Murugaiyan G, Doykan CE, Wu PM, Gali RR, Iyer LK, Lawson R, Berry J, Krichevsky AM, Cudkowicz ME, Weiner HL. Modulating inflammatory monocytes with a unique microRNA gene signature ameliorates murine ALS. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:3063–3087. doi: 10.1172/JCI62636. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Castello NA, Nguyen MH, Tran JD, Cheng D, Green KN, LaFerla FM. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone, a small molecule TrkB agonist, improves spatial memory and increases thin spine density in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease-like neuronal loss. PloS One. 2014;9:e91453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091453. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
