Rosuvastatin Worsens Insulin Resistance in HIV-Infected Adults on Antiretroviral Therapy
- PMID: 26157049
- PMCID: PMC4614408
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/civ554
Rosuvastatin Worsens Insulin Resistance in HIV-Infected Adults on Antiretroviral Therapy
Abstract
Background: Statins are associated with increased diabetes risk in large, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-uninfected cohorts; the impact of statins on insulin resistance or diabetes in HIV-infected persons has not been assessed within a randomized controlled study.
Methods: HIV-infected participants on stable antiretroviral therapy with a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level of ≤130 mg/dL and heightened immune activation or inflammation were randomized to rosuvastatin 10 mg daily or placebo for 96 weeks. Fasting serum glucose, insulin, and hemoglobin A1C (HgbA1C) were measured; insulin resistance was estimated by calculating the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR); and a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test was administered.
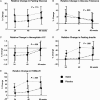
Results: Seventy-two participants were randomized to rosuvastatin therapy and 75 to placebo. Increases in fasting glucose were observed within both groups but were not different between study arms (P = .115); changes in glucose tolerance and HgbA1C did not differ between study arms (P = .920 and P = .650, respectively). Criteria for diabetes were met by 1 participant in the rosuvastatin and 3 in the placebo arm by week 96. Compared with placebo, rosuvastatin therapy was associated with significantly greater increases in insulin and HOMA-IR (P = .008 and P = .004, respectively).
Conclusions: We detected a significant worsening in insulin resistance and an increase in the proportion of participants with impaired fasting glucose but not a clinical diagnosis of diabetes in the rosuvastatin arm. Our findings suggest that prescription of statin therapy should be accompanied by a careful consideration of the risks and benefits, particularly in patients with lower cardiovascular disease risk.
Clinical trials registration: NCT01218802.
Keywords: HOMA-IR; glucose metabolism; inflammation; insulin resistance; statin.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Metkus TS Jr, Brown TT, Post WS. Cardiovascular disease associated with the human immunodeficiency virus: an update. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 2014; 16:346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

