Identification, Functional Characterization, and Evolution of Terpene Synthases from a Basal Dicot
- PMID: 26157114
- PMCID: PMC4634067
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.00930
Identification, Functional Characterization, and Evolution of Terpene Synthases from a Basal Dicot
Abstract
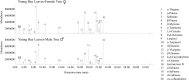
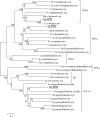
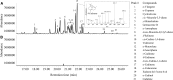
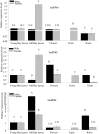
Bay laurel (Laurus nobilis) is an agriculturally and economically important dioecious tree in the basal dicot family Lauraceae used in food and drugs and in the cosmetics industry. Bay leaves, with their abundant monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, are used to impart flavor and aroma to food, and have also drawn attention in recent years because of their potential pharmaceutical applications. To identify terpene synthases (TPSs) involved in the production of these volatile terpenes, we performed RNA sequencing to profile the transcriptome of L. nobilis leaves. Bioinformatic analysis led to the identification of eight TPS complementary DNAs. We characterized the enzymes encoded by three of these complementary DNAs: a monoterpene synthase that belongs to the TPS-b clade catalyzes the formation of mostly 1,8-cineole; a sesquiterpene synthase belonging to the TPS-a clade catalyzes the formation of mainly cadinenes; and a diterpene synthase of the TPS-e/f clade catalyzes the formation of geranyllinalool. Comparison of the sequences of these three TPSs indicated that the TPS-a and TPS-b clades of the TPS gene family evolved early in the evolution of the angiosperm lineage, and that geranyllinalool synthase activity is the likely ancestral function in angiosperms of genes belonging to an ancient TPS-e/f subclade that diverged from the kaurene synthase gene lineages before the split of angiosperms and gymnosperms.
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Geranyllinalool synthases in solanaceae and other angiosperms constitute an ancient branch of diterpene synthases involved in the synthesis of defensive compounds.Plant Physiol. 2014 Sep;166(1):428-41. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.243246. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25052853 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of volatile terpenes from almond (Prunus dulcis) young fruits and characterization of seven terpene synthase genes.Plant Sci. 2019 Oct;287:110187. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110187. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31481200
-
Terpenoid secondary metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana: cDNA cloning, characterization, and functional expression of a myrcene/(E)-beta-ocimene synthase.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000 Mar 15;375(2):261-9. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1669. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 10700382
-
The family of terpene synthases in plants: a mid-size family of genes for specialized metabolism that is highly diversified throughout the kingdom.Plant J. 2011 Apr;66(1):212-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04520.x. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21443633 Review.
-
On the Evolution and Functional Diversity of Terpene Synthases in the Pinus Species: A Review.J Mol Evol. 2020 Apr;88(3):253-283. doi: 10.1007/s00239-020-09930-8. Epub 2020 Feb 8. J Mol Evol. 2020. PMID: 32036402 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Potential of FT-IR Fingerprinting in Botanical Origin Evaluation of Laurus nobilis L. Essential Oil is Supported by GC-FID-MS Data.Molecules. 2020 Jan 29;25(3):583. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030583. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32013186 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterisation of New Sesquiterpene Synthase from the Malaysian Herbal Plant, Polygonum Minus.Molecules. 2018 Jun 6;23(6):1370. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061370. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29882808 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide detection of terpene synthase genes in holy basil (Ocimum sanctum L.).PLoS One. 2018 Nov 16;13(11):e0207097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207097. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30444870 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Botany, Volatile Composition, Biochemical and Molecular Aspects, and Traditional Uses of Laurus nobilis.Plants (Basel). 2022 Apr 29;11(9):1209. doi: 10.3390/plants11091209. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35567209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of expressed sequence tags for discovery of genes responsible for floral traits of Chrysanthemum morifolium by next-generation sequencing technology.BMC Genomics. 2017 Sep 4;18(1):683. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4061-3. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28870156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianchini GM, Stipanovic RD, Bell AA (1999) Induction of delta-cadinene synthase and sesquiterpenoid phytoalexins in cotton by Verticillium dahliae. J Agric Food Chem 47: 4403–4406 - PubMed
-
- Boland W, Gabler A (1989) Biosynthesis of homoterpenes in higher plants. Helv Chim Acta 72: 247–253
-
- Brandt W, Bräuer L, Günnewich N, Kufka J, Rausch F, Schulze D, Schulze E, Weber R, Zakharova S, Wessjohann L (2009) Molecular and structural basis of metabolic diversity mediated by prenyldiphosphate converting enzymes. Phytochemistry 70: 1758–1775 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

