Cutting Edge: Redox Signaling Hypersensitivity Distinguishes Human Germinal Center B Cells
- PMID: 26157177
- PMCID: PMC4530023
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500904
Cutting Edge: Redox Signaling Hypersensitivity Distinguishes Human Germinal Center B Cells
Abstract
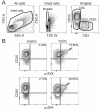
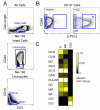
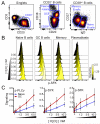
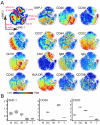
Differences in the quality of BCR signaling control key steps of B cell maturation and differentiation. Endogenously produced H2O2 is thought to fine tune the level of BCR signaling by reversibly inhibiting phosphatases. However, relatively little is known about how B cells at different stages sense and respond to such redox cues. In this study, we used phospho-specific flow cytometry and high-dimensional mass cytometry (CyTOF) to compare BCR signaling responses in mature human tonsillar B cells undergoing germinal center (GC) reactions. GC B cells, in contrast to mature naive B cells, memory B cells, and plasmablasts, were hypersensitive to a range of H2O2 concentrations and responded by phosphorylating SYK and other membrane-proximal BCR effectors in the absence of BCR engagement. These findings reveal that stage-specific redox responses distinguish human GC B cells.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Reth M. Hydrogen Peroxide as a second messenger in lymphocyte activation. Nat Immunol. 2002:3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

