A reproducible approach to high-throughput biological data acquisition and integration
- PMID: 26157642
- PMCID: PMC4493686
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.791
A reproducible approach to high-throughput biological data acquisition and integration
Abstract
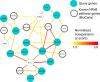
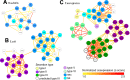
Modern biological research requires rapid, complex, and reproducible integration of multiple experimental results generated both internally and externally (e.g., from public repositories). Although large systematic meta-analyses are among the most effective approaches both for clinical biomarker discovery and for computational inference of biomolecular mechanisms, identifying, acquiring, and integrating relevant experimental results from multiple sources for a given study can be time-consuming and error-prone. To enable efficient and reproducible integration of diverse experimental results, we developed a novel approach for standardized acquisition and analysis of high-throughput and heterogeneous biological data. This allowed, first, novel biomolecular network reconstruction in human prostate cancer, which correctly recovered and extended the NFκB signaling pathway. Next, we investigated host-microbiome interactions. In less than an hour of analysis time, the system retrieved data and integrated six germ-free murine intestinal gene expression datasets to identify the genes most influenced by the gut microbiota, which comprised a set of immune-response and carbohydrate metabolism processes. Finally, we constructed integrated functional interaction networks to compare connectivity of peptide secretion pathways in the model organisms Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Keywords: Data acquisition; Data integration; Heterogeneous data; High-throughput data; Meta-analysis; Reproducibility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Affymetrix . Statistical algorithms description document. Santa Clara: Affymetrix Inc; 2002.
-
- Aoyama T, Peters JM, Iritani N, Nakajima T, Furihata K, Hashimoto T, Gonzalez FJ. Altered constitutive expression of fatty acid-metabolizing enzymes in mice lacking the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1998;273:5678–5684. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.10.5678. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:15718–15723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407076101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baggerly KA, Coombes KR. Deriving chemosensitivity from cell lines: forensic bioinformatics and reproducible research in high-throughput biology. The Annals of Applied Statistics. 2009;3:1309–1334. doi: 10.1214/09-AOAS291. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

