Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: A Current Update on Non-Conventional Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Interventions
- PMID: 26157666
- PMCID: PMC4494988
- DOI: 10.14581/jer.15001
Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: A Current Update on Non-Conventional Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Abstract
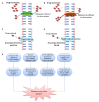
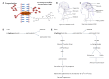
Uncontrolled seizure or epilepsy is intricately related with an increase risk of pharmacoresistant epilepsy. The failure to achieve seizure control with the first or second drug trial of an anticonvulsant medication given at the appropriate daily dosage is termed as pharmacoresistance, despite the fact that these drugs possess different modes of action. It is one of the devastating neurological disorders act as major culprit of mortality in developed as well as developing countries with towering prevalence. Indeed, the presence of several anti-epileptic drug including carbamazepine, phenytoin, valproate, gabapentin etc. But no promising therapeutic remedies available to manage pharmacoresistance in the present clinical scenario. Hence, utility of alternative strategies in management of resistance epilepsy is increased which further possible by continuing developing of promising therapeutic interventions to manage this insidious condition adequately. Strategies include add on therapy with adenosine, verapamil etc or ketogenic diet, vagus nerve stimulation, focal cooling or standard drugs in combinations have shown some promising results. In this review we will shed light on the current pharmacological and non pharmacological mediator with their potential pleiotropic action on pharmacoresistant epilepsy.
Keywords: Adenosine; Drug resistant epilepsy; Modified Atkins diet; Responsive neurostimulation; Thyrotropin releasing hormone.
Figures
References
-
- Czapinski P, Blaszczyk B. Mechanisms of Action of Antiepileptic Drugs. Curr Top Med Chem. 2005;5:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Rajput SK, Singh JN, Ingole S, et al. Neuropharmacological profile of L-pGlu-(1-benzyl)- L-His-L-ProNH2, a newer thyrotropin-releasing hormone analog: Effects on seizure models, sodium current, cerebral blood flow and behavioural parameters. Epilepsy Res. 2009;87:223–33. - PubMed
-
- Andreas V. Alexopoulos. Pharmacoresistant epilepsy: Definition and explanation. Epileptology. 2013;1:38–42.
-
- Duncan JS, Sander JW, Sisodiya SM, Walker MC. Adult Epilepsy. Lancet. 2006;367:1087–187. - PubMed
-
- Arts WF, Brouwer OF, Peters AC, et al. Course and prognosis of childhood epilepsy: 5-year follow-up of the Dutch study of epilepsy in childhood. Brain. 2004;127:177–484. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

