The protective effects of trace elements against side effects induced by ionizing radiation
- PMID: 26157675
- PMCID: PMC4493430
- DOI: 10.3857/roj.2015.33.2.66
The protective effects of trace elements against side effects induced by ionizing radiation
Abstract
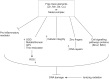
Trace elements play crucial role in the maintenance of genome stability in the cells. Many endogenous defense enzymes are containing trace elements such as superoxide dismutase and metalloproteins. These enzymes are contributing in the detoxification of reactive oxidative species (ROS) induced by ionizing radiation in the cells. Zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium are main trace elements that have protective roles against radiation-induced DNA damages. Trace elements in the free salt forms have protective effect against cell toxicity induced by oxidative stress, metal-complex are more active in the attenuation of ROS particularly through superoxide dismutase mimetic activity. Manganese-complexes in protection of normal cell against radiation without any protective effect on cancer cells are more interesting compounds in this topic. The aim of this paper to review the role of trace elements in protection cells against genotoxicity and side effects induced by ionizing radiation.
Keywords: DNA damage; Radiation; Radiation-protective agent; Side effects; Trace elements.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A manganese porphyrin complex is a novel radiation protector.Free Radic Biol Med. 2004 Jul 15;37(2):272-83. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.04.029. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004. PMID: 15203198
-
Trace elements as an activator of antioxidant enzymes.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016 Dec 31;70(0):1483-1498. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1229074. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016. PMID: 28100855 Review.
-
[Enhancement of endogenous antioxidant defenses: a promising strategy for prevention of skin cancers].Bull Acad Natl Med. 2001;185(8):1507-25; discussion 1526-7. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2001. PMID: 11974970 French.
-
Copper- and zinc-containing superoxide dismutase, manganese-containing superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase in normal and neoplastic human cell lines and normal human tissues.Cancer Res. 1982 May;42(5):1955-61. Cancer Res. 1982. PMID: 7066906
-
Role of copper, zinc, selenium and tellurium in the cellular defense against oxidative and nitrosative stress.J Nutr. 2003 May;133(5 Suppl 1):1448S-51S. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.5.1448S. J Nutr. 2003. PMID: 12730440 Review.
Cited by
-
Radioprotective Effect of Piperine, as a Major Component of Black Pepper, Against Radiation-induced Colon Injury: Biochemical and Histological Studies.Curr Radiopharm. 2024;17(1):38-45. doi: 10.2174/1874471016666230725112319. Curr Radiopharm. 2024. PMID: 37489775
-
Effects of Ionizing Radiation on Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) in the Presence of Mentha-Pulegium Essential Oil: A Study on the Radioprotective Effect.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2022 Apr 1;12(2):137-148. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2109-1397. eCollection 2022 Apr. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2022. PMID: 35433518 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of salivary gland dysfunction in patients treated with radioiodine for differentiated thyroid cancer: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 29;13:960265. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.960265. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36105397 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Discovery Targeting Post-Translational Modifications in Response to DNA Damages Induced by Space Radiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 21;24(8):7656. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087656. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HMGB1 knockdown increases the radiosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the expression of molecules involved in DNA repair.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jul;22(1):503. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12764. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33986864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hosseinimehr SJ. Flavonoids and genomic instability induced by ionizing radiation. Drug Discov Today. 2010;15:907–918. - PubMed
-
- Limon-Pacheco J, Gonsebatt ME. The role of antioxidants and antioxidant-related enzymes in protective responses to environmentally induced oxidative stress. Mutat Res. 2009;674:137–147. - PubMed
-
- Frassinetti S, Bronzetti G, Caltavuturo L, Cini M, Croce CD. The role of zinc in life: a review. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2006;25:597–610. - PubMed
-
- Ho E. Zinc deficiency, DNA damage and cancer risk. J Nutr Biochem. 2004;15:572–578. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources