Clinical, Biochemical, and Genetic Characterization of Glycogen Storage Type IX in a Child with Asymptomatic Hepatomegaly
- PMID: 26157701
- PMCID: PMC4493248
- DOI: 10.5223/pghn.2015.18.2.138
Clinical, Biochemical, and Genetic Characterization of Glycogen Storage Type IX in a Child with Asymptomatic Hepatomegaly
Abstract
Glycogen storage disease type IX (GSD IX) is caused by a defect in phosphorylase b kinase (PhK) that results from mutations in the PHKA2, PHKB, and PHKG2 genes. Patients usually manifest recurrent ketotic hypoglycemia with growth delay, but some may present simple hepatomegaly. Although GSD IX is one of the most common causes of GSDs, its biochemical and genetic diagnosis has been problematic due to its rarity, phenotypic overlap with other types of GSDs, and genetic heterogeneities. In our report, a 22-month-old boy with GSD IX is described. No other manifestations were evident except for hepatomegaly. His growth and development also have been proceeding normally. Diagnosed was made by histologic examination, an enzyme assay, and genetic testing with known c.3210_3212del (p.Arg1070del) mutation in PHKA2 gene.
Keywords: Glycogen storage disease; Glycogen storage disease type IX; Hepatomegaly; Phosphorylase b kinase 2; Phosphorylase kinase.
Figures
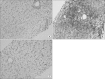
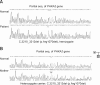
References
-
- Lau CK, Hui J, Fong FN, To KF, Fok TF, Tang NL, et al. Novel mutations in PHKA2 gene in glycogen storage disease type IX patients from Hong Kong, China. Mol Genet Metab. 2011;102:222–225. - PubMed
-
- Maichele AJ, Burwinkel B, Maire I, Søvik O, Kilimann MW. Mutations in the testis/liver isoform of the phosphorylase kinase gamma subunit (PHKG2) cause autosomal liver glycogenosis in the gsd rat and in humans. Nat Genet. 1996;14:337–340. - PubMed
-
- Newgard CB, Hwang PK, Fletterick RJ. The family of glycogen phosphorylases: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1989;24:69–99. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources