Multireader multicase reader studies with binary agreement data: simulation, analysis, validation, and sizing
- PMID: 26158051
- PMCID: PMC4478886
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.1.3.031011
Multireader multicase reader studies with binary agreement data: simulation, analysis, validation, and sizing
Abstract
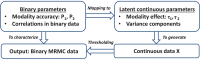
We treat multireader multicase (MRMC) reader studies for which a reader's diagnostic assessment is converted to binary agreement (1: agree with the truth state, 0: disagree with the truth state). We present a mathematical model for simulating binary MRMC data with a desired correlation structure across readers, cases, and two modalities, assuming the expected probability of agreement is equal for the two modalities ([Formula: see text]). This model can be used to validate the coverage probabilities of 95% confidence intervals (of [Formula: see text], [Formula: see text], or [Formula: see text] when [Formula: see text]), validate the type I error of a superiority hypothesis test, and size a noninferiority hypothesis test (which assumes [Formula: see text]). To illustrate the utility of our simulation model, we adapt the Obuchowski-Rockette-Hillis (ORH) method for the analysis of MRMC binary agreement data. Moreover, we use our simulation model to validate the ORH method for binary data and to illustrate sizing in a noninferiority setting. Our software package is publicly available on the Google code project hosting site for use in simulation, analysis, validation, and sizing of MRMC reader studies with binary agreement data.
Keywords: Monte Carlo simulation; binary data; multireader multicase; reader study; sizing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between Obuchowski-Rockette-Hillis and Gallas methods for analyzing multi-reader diagnostic imaging data with empirical AUC as the reader performance measure.Biostat Epidemiol. 2023;7(1):e2062115. doi: 10.1080/24709360.2022.2062115. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Biostat Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 37719421 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothesis testing in noninferiority and equivalence MRMC ROC studies.Acad Radiol. 2012 Sep;19(9):1158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2012.04.011. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Acad Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22717591
-
Identical-test Roe and Metz simulation model for validating multi-reader methods of analysis for comparing different radiologic imaging modalities.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2022 Feb-Mar;12035:120350E. doi: 10.1117/12.2612691. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2022. PMID: 36159879 Free PMC article.
-
Determining Roe and Metz model parameters for simulating multireader multicase confidence-of-disease rating data based on real-data or conjectured Obuchowski-Rockette parameter estimates.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2022 Jul;9(4):045501. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.9.4.045501. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2022. PMID: 35818569 Free PMC article.
-
Multireader Diagnostic Accuracy Imaging Studies: Fundamentals of Design and Analysis.Radiology. 2022 Apr;303(1):26-34. doi: 10.1148/radiol.211593. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Radiology. 2022. PMID: 35166584 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Quality of 3D T2-SPACE Compared with T2-FSE in the Evaluation of Cervical Spine MRI Anatomy.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017 Apr;38(4):846-850. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5080. Epub 2017 Feb 2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 28154126 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective Multi-Site Validation of AI to Detect Tuberculosis and Chest X-Ray Abnormalities.NEJM AI. 2024 Oct;1(10):10.1056/aioa2400018. doi: 10.1056/aioa2400018. Epub 2024 Sep 26. NEJM AI. 2024. PMID: 39823016 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Roe and Metz simulation model for multireader diagnostic data and Obuchowski-Rockette model parameters.Stat Med. 2018 Jun 15;37(13):2067-2093. doi: 10.1002/sim.7616. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Stat Med. 2018. PMID: 29609206 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory considerations for medical imaging AI/ML devices in the United States: concepts and challenges.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2023 Sep;10(5):051804. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.10.5.051804. Epub 2023 Jun 23. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2023. PMID: 37361549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between Obuchowski-Rockette-Hillis and Gallas methods for analyzing multi-reader diagnostic imaging data with empirical AUC as the reader performance measure.Biostat Epidemiol. 2023;7(1):e2062115. doi: 10.1080/24709360.2022.2062115. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Biostat Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 37719421 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

